category.json
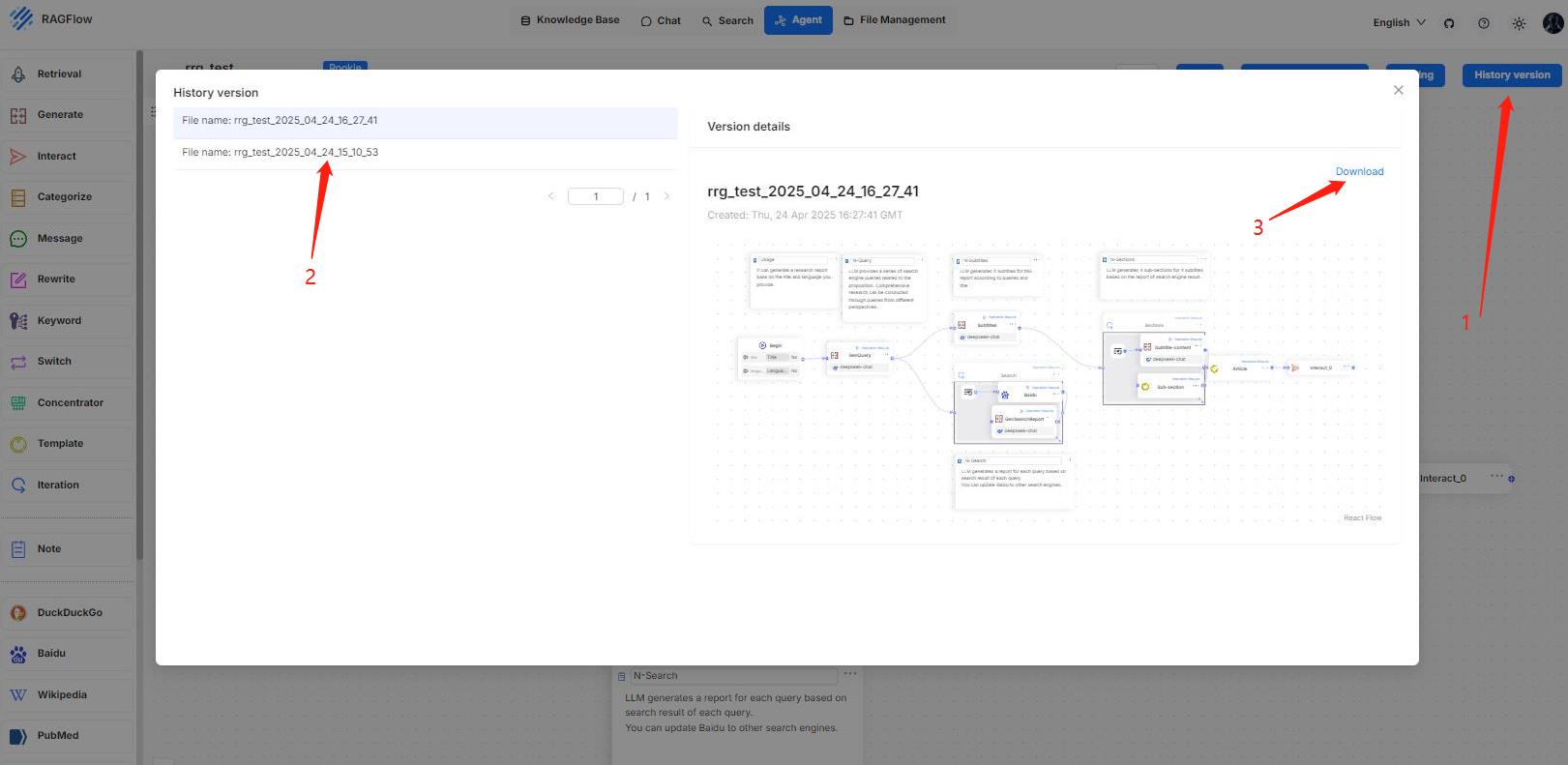
{
"label": "Get Started",
"position": 1,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "RAGFlow Quick Start"
}
}
configurations.md
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /configurations
---
# Configuration
Configurations for deploying RAGFlow via Docker.
## Guidelines
When it comes to system configurations, you will need to manage the following files:
- [.env](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/.env): Contains important environment variables for Docker.
- [service_conf.yaml.template](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/service_conf.yaml.template): Configures the back-end services. It specifies the system-level configuration for RAGFlow and is used by its API server and task executor. Upon container startup, the `service_conf.yaml` file will be generated based on this template file. This process replaces any environment variables within the template, allowing for dynamic configuration tailored to the container's environment.
- [docker-compose.yml](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/docker-compose.yml): The Docker Compose file for starting up the RAGFlow service.
To update the default HTTP serving port (80), go to [docker-compose.yml](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/docker-compose.yml) and change `80:80`
to `<YOUR_SERVING_PORT>:80`.
:::tip NOTE
Updates to the above configurations require a reboot of all containers to take effect:
```bash
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -d
```
:::
## Docker Compose
- **docker-compose.yml**
Sets up environment for RAGFlow and its dependencies.
- **docker-compose-base.yml**
Sets up environment for RAGFlow's dependencies: Elasticsearch/[Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity), MySQL, MinIO, and Redis.
:::danger IMPORTANT
We do not actively maintain **docker-compose-CN-oc9.yml**, **docker-compose-gpu-CN-oc9.yml**, or **docker-compose-gpu.yml**, so use them at your own risk. However, you are welcome to file a pull request to improve any of them.
:::
## Docker environment variables
The [.env](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/.env) file contains important environment variables for Docker.
### Elasticsearch
- `STACK_VERSION`
The version of Elasticsearch. Defaults to `8.11.3`
- `ES_PORT`
The port used to expose the Elasticsearch service to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the service running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `1200`.
- `ELASTIC_PASSWORD`
The password for Elasticsearch.
### Kibana
- `KIBANA_PORT`
The port used to expose the Kibana service to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the service running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `6601`.
- `KIBANA_USER`
The username for Kibana. Defaults to `rag_flow`.
- `KIBANA_PASSWORD`
The password for Kibana. Defaults to `infini_rag_flow`.
### Resource management
- `MEM_LIMIT`
The maximum amount of the memory, in bytes, that *a specific* Docker container can use while running. Defaults to `8073741824`.
### MySQL
- `MYSQL_PASSWORD`
The password for MySQL.
- `MYSQL_PORT`
The port used to expose the MySQL service to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the MySQL database running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `5455`.
### MinIO
RAGFlow utilizes MinIO as its object storage solution, leveraging its scalability to store and manage all uploaded files.
- `MINIO_CONSOLE_PORT`
The port used to expose the MinIO console interface to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the web-based console running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `9001`
- `MINIO_PORT`
The port used to expose the MinIO API service to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the MinIO object storage service running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `9000`.
- `MINIO_USER`
The username for MinIO.
- `MINIO_PASSWORD`
The password for MinIO.
### Redis
- `REDIS_PORT`
The port used to expose the Redis service to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the Redis service running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `6379`.
- `REDIS_PASSWORD`
The password for Redis.
### RAGFlow
- `SVR_HTTP_PORT`
The port used to expose RAGFlow's HTTP API service to the host machine, allowing **external** access to the service running inside the Docker container. Defaults to `9380`.
- `RAGFLOW-IMAGE`
The Docker image edition. Available editions:
- `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0-slim` (default): The RAGFlow Docker image without embedding models.
- `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0`: The RAGFlow Docker image with embedding models including:
- Built-in embedding models:
- `BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5`
- `maidalun1020/bce-embedding-base_v1`
:::tip NOTE
If you cannot download the RAGFlow Docker image, try the following mirrors.
- For the `nightly-slim` edition:
- `RAGFLOW_IMAGE=swr.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/infiniflow/ragflow:nightly-slim` or,
- `RAGFLOW_IMAGE=registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/infiniflow/ragflow:nightly-slim`.
- For the `nightly` edition:
- `RAGFLOW_IMAGE=swr.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/infiniflow/ragflow:nightly` or,
- `RAGFLOW_IMAGE=registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/infiniflow/ragflow:nightly`.
:::
### Timezone
- `TIMEZONE`
The local time zone. Defaults to `'Asia/Shanghai'`.
### Hugging Face mirror site
- `HF_ENDPOINT`
The mirror site for huggingface.co. It is disabled by default. You can uncomment this line if you have limited access to the primary Hugging Face domain.
### MacOS
- `MACOS`
Optimizations for macOS. It is disabled by default. You can uncomment this line if your OS is macOS.
### User registration
- `REGISTER_ENABLED`
- `1`: (Default) Enable user registration.
- `0`: Disable user registration.
## Service configuration
[service_conf.yaml.template](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/service_conf.yaml.template) specifies the system-level configuration for RAGFlow and is used by its API server and task executor.
### `ragflow`
- `host`: The API server's IP address inside the Docker container. Defaults to `0.0.0.0`.
- `port`: The API server's serving port inside the Docker container. Defaults to `9380`.
### `mysql`
- `name`: The MySQL database name. Defaults to `rag_flow`.
- `user`: The username for MySQL.
- `password`: The password for MySQL.
- `port`: The MySQL serving port inside the Docker container. Defaults to `3306`.
- `max_connections`: The maximum number of concurrent connections to the MySQL database. Defaults to `100`.
- `stale_timeout`: Timeout in seconds.
### `minio`
- `user`: The username for MinIO.
- `password`: The password for MinIO.
- `host`: The MinIO serving IP *and* port inside the Docker container. Defaults to `minio:9000`.
### `oauth`
The OAuth configuration for signing up or signing in to RAGFlow using a third-party account. It is disabled by default. To enable this feature, uncomment the corresponding lines in **service_conf.yaml.template**.
- `github`: The GitHub authentication settings for your application. Visit the [GitHub Developer Settings](https://github.com/settings/developers) page to obtain your client_id and secret_key.
#### OAuth/OIDC
RAGFlow supports OAuth/OIDC authentication through the following routes:
- `/login/<channel>`: Initiates the OAuth flow for the specified channel
- `/oauth/callback/<channel>`: Handles the OAuth callback after successful authentication
The callback URL should be configured in your OAuth provider as:
```
https://your-app.com/oauth/callback/<channel>
```
For detailed instructions on configuring **service_conf.yaml.template**, please refer to [Usage](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/api/apps/auth/README.md#usage).
### `user_default_llm`
The default LLM to use for a new RAGFlow user. It is disabled by default. To enable this feature, uncomment the corresponding lines in **service_conf.yaml.template**.
- `factory`: The LLM supplier. Available options:
- `"OpenAI"`
- `"DeepSeek"`
- `"Moonshot"`
- `"Tongyi-Qianwen"`
- `"VolcEngine"`
- `"ZHIPU-AI"`
- `api_key`: The API key for the specified LLM. You will need to apply for your model API key online.
:::tip NOTE
If you do not set the default LLM here, configure the default LLM on the **Settings** page in the RAGFlow UI.
:::
faq.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 10
slug: /faq
---
# FAQs
Answers to questions about general features, troubleshooting, usage, and more.
---
import TOCInline from '@theme/TOCInline';
<TOCInline toc={toc} />
## General features
---
### What sets RAGFlow apart from other RAG products?
The "garbage in garbage out" status quo remains unchanged despite the fact that LLMs have advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) significantly. In response, RAGFlow introduces two unique features compared to other Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) products.
- Fine-grained document parsing: Document parsing involves images and tables, with the flexibility for you to intervene as needed.
- Traceable answers with reduced hallucinations: You can trust RAGFlow's responses as you can view the citations and references supporting them.
---
### Differences between RAGFlow full edition and RAGFlow slim edition?
Each RAGFlow release is available in two editions:
- **Slim edition**: excludes built-in embedding models and is identified by a **-slim** suffix added to the version name. Example: `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0-slim`
- **Full edition**: includes built-in embedding models and has no suffix added to the version name. Example: `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0`
---
### Which embedding models can be deployed locally?
RAGFlow offers two Docker image editions, `v0.18.0-slim` and `v0.18.0`:
- `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0-slim` (default): The RAGFlow Docker image without embedding models.
- `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0`: The RAGFlow Docker image with embedding models including:
- Built-in embedding models:
- `BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5`
- `maidalun1020/bce-embedding-base_v1`
- Embedding models that will be downloaded once you select them in the RAGFlow UI:
- `BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5`
- `BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5`
- `BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5`
- `BAAI/bge-small-zh-v1.5`
- `jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-base-en`
- `jinaai/jina-embeddings-v2-small-en`
- `nomic-ai/nomic-embed-text-v1.5`
- `sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2`
---
### Where to find the version of RAGFlow? How to interpret it?
You can find the RAGFlow version number on the **System** page of the UI:

If you build RAGFlow from source, the version number is also in the system log:
```
____ ___ ______ ______ __
/ __ \ / | / ____// ____// /____ _ __
/ /_/ // /| | / / __ / /_ / // __ \| | /| / /
/ _, _// ___ |/ /_/ // __/ / // /_/ /| |/ |/ /
/_/ |_|/_/ |_|\____//_/ /_/ \____/ |__/|__/
2025-02-18 10:10:43,835 INFO 1445658 RAGFlow version: v0.15.0-50-g6daae7f2 full
```
Where:
- `v0.15.0`: The officially published release.
- `50`: The number of git commits since the official release.
- `g6daae7f2`: `g` is the prefix, and `6daae7f2` is the first seven characters of the current commit ID.
- `full`/`slim`: The RAGFlow edition.
- `full`: The full RAGFlow edition.
- `slim`: The RAGFlow edition without embedding models and Python packages.
---
### Differences between demo.ragflow.io and a locally deployed open-source RAGFlow service?
demo.ragflow.io demonstrates the capabilities of RAGFlow Enterprise. Its DeepDoc models are pre-trained using proprietary data and it offers much more sophisticated team permission controls. Essentially, demo.ragflow.io serves as a preview of RAGFlow's forthcoming SaaS (Software as a Service) offering.
You can deploy an open-source RAGFlow service and call it from a Python client or through RESTful APIs. However, this is not supported on demo.ragflow.io.
---
### Why does it take longer for RAGFlow to parse a document than LangChain?
We put painstaking effort into document pre-processing tasks like layout analysis, table structure recognition, and OCR (Optical Character Recognition) using our vision models. This contributes to the additional time required.
---
### Why does RAGFlow require more resources than other projects?
RAGFlow has a number of built-in models for document structure parsing, which account for the additional computational resources.
---
### Which architectures or devices does RAGFlow support?
We officially support x86 CPU and nvidia GPU. While we also test RAGFlow on ARM64 platforms, we do not maintain RAGFlow Docker images for ARM. If you are on an ARM platform, follow [this guide](./develop/build_docker_image.mdx) to build a RAGFlow Docker image.
---
### Do you offer an API for integration with third-party applications?
The corresponding APIs are now available. See the [RAGFlow HTTP API Reference](./references/http_api_reference.md) or the [RAGFlow Python API Reference](./references/python_api_reference.md) for more information.
---
### Do you support stream output?
Yes, we do.
---
### Do you support sharing dialogue through URL?
No, this feature is not supported.
---
### Do you support multiple rounds of dialogues, referencing previous dialogues as context for the current query?
Yes, we support enhancing user queries based on existing context of an ongoing conversation:
1. On the **Chat** page, hover over the desired assistant and select **Edit**.
2. In the **Chat Configuration** popup, click the **Prompt engine** tab.
3. Switch on **Multi-turn optimization** to enable this feature.
---
### Key differences between AI search and chat?
- **AI search**: This is a single-turn AI conversation using a predefined retrieval strategy (a hybrid search of weighted keyword similarity and weighted vector similarity) and the system's default chat model. It does not involve advanced RAG strategies like knowledge graph, auto-keyword, or auto-question. Retrieved chunks will be listed below the chat model's response.
- **AI chat**: This is a multi-turn AI conversation where you can define your retrieval strategy (a weighted reranking score can be used to replace the weighted vector similarity in a hybrid search) and choose your chat model. In an AI chat, you can configure advanced RAG strategies, such as knowledge graphs, auto-keyword, and auto-question, for your specific case. Retrieved chunks are not displayed along with the answer.
When debugging your chat assistant, you can use AI search as a reference to verify your model settings and retrieval strategy.
---
## Troubleshooting
---
### How to build the RAGFlow image from scratch?
See [Build a RAGFlow Docker image](./develop/build_docker_image.mdx).
### Cannot access https://huggingface.co
A locally deployed RAGflow downloads OCR and embedding modules from [Huggingface website](https://huggingface.co) by default. If your machine is unable to access this site, the following error occurs and PDF parsing fails:
```
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/root/.cache/huggingface/hub/models--InfiniFlow--deepdoc/snapshots/be0c1e50eef6047b412d1800aa89aba4d275f997/ocr.res'
```
To fix this issue, use https://hf-mirror.com instead:
1. Stop all containers and remove all related resources:
```bash
cd ragflow/docker/
docker compose down
```
2. Uncomment the following line in **ragflow/docker/.env**:
```
# HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
```
3. Start up the server:
```bash
docker compose up -d
```
---
### `MaxRetryError: HTTPSConnectionPool(host='hf-mirror.com', port=443)`
This error suggests that you do not have Internet access or are unable to connect to hf-mirror.com. Try the following:
1. Manually download the resource files from [huggingface.co/InfiniFlow/deepdoc](https://huggingface.co/InfiniFlow/deepdoc) to your local folder **~/deepdoc**.
2. Add a volumes to **docker-compose.yml**, for example:
```
- ~/deepdoc:/ragflow/rag/res/deepdoc
```
---
### `WARNING: can't find /raglof/rag/res/borker.tm`
Ignore this warning and continue. All system warnings can be ignored.
---
### `network anomaly There is an abnormality in your network and you cannot connect to the server.`

You will not log in to RAGFlow unless the server is fully initialized. Run `docker logs -f ragflow-server`.
*The server is successfully initialized, if your system displays the following:*
```
____ ___ ______ ______ __
/ __ \ / | / ____// ____// /____ _ __
/ /_/ // /| | / / __ / /_ / // __ \| | /| / /
/ _, _// ___ |/ /_/ // __/ / // /_/ /| |/ |/ /
/_/ |_|/_/ |_|\____//_/ /_/ \____/ |__/|__/
* Running on all addresses (0.0.0.0)
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:9380
* Running on http://x.x.x.x:9380
INFO:werkzeug:Press CTRL+C to quit
```
---
### `Realtime synonym is disabled, since no redis connection`
Ignore this warning and continue. All system warnings can be ignored.

---
### Why does my document parsing stall at under one percent?

Click the red cross beside the 'parsing status' bar, then restart the parsing process to see if the issue remains. If the issue persists and your RAGFlow is deployed locally, try the following:
1. Check the log of your RAGFlow server to see if it is running properly:
```bash
docker logs -f ragflow-server
```
2. Check if the **task_executor.py** process exists.
3. Check if your RAGFlow server can access hf-mirror.com or huggingface.com.
---
### Why does my pdf parsing stall near completion, while the log does not show any error?
Click the red cross beside the 'parsing status' bar, then restart the parsing process to see if the issue remains. If the issue persists and your RAGFlow is deployed locally, the parsing process is likely killed due to insufficient RAM. Try increasing your memory allocation by increasing the `MEM_LIMIT` value in **docker/.env**.
:::note
Ensure that you restart up your RAGFlow server for your changes to take effect!
```bash
docker compose stop
```
```bash
docker compose up -d
```
:::

---
### `Index failure`
An index failure usually indicates an unavailable Elasticsearch service.
---
### How to check the log of RAGFlow?
```bash
tail -f ragflow/docker/ragflow-logs/*.log
```
---
### How to check the status of each component in RAGFlow?
1. Check the status of the Elasticsearch Docker container:
```bash
$ docker ps
```
*The following is an example result:*
```bash
5bc45806b680 infiniflow/ragflow:latest "./entrypoint.sh" 11 hours ago Up 11 hours 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, :::80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp, :::443->443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9380->9380/tcp, :::9380->9380/tcp ragflow-server
91220e3285dd docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.11.3 "/bin/tini -- /usr/l…" 11 hours ago Up 11 hours (healthy) 9300/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9200->9200/tcp, :::9200->9200/tcp ragflow-es-01
d8c86f06c56b mysql:5.7.18 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 7 days ago Up 16 seconds (healthy) 0.0.0.0:3306->3306/tcp, :::3306->3306/tcp ragflow-mysql
cd29bcb254bc quay.io/minio/minio:RELEASE.2023-12-20T01-00-02Z "/usr/bin/docker-ent…" 2 weeks ago Up 11 hours 0.0.0.0:9001->9001/tcp, :::9001->9001/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, :::9000->9000/tcp ragflow-minio
```
2. Follow [this document](./guides/run_health_check.md) to check the health status of the Elasticsearch service.
:::danger IMPORTANT
The status of a Docker container status does not necessarily reflect the status of the service. You may find that your services are unhealthy even when the corresponding Docker containers are up running. Possible reasons for this include network failures, incorrect port numbers, or DNS issues.
:::
---
### `Exception: Can't connect to ES cluster`
1. Check the status of the Elasticsearch Docker container:
```bash
$ docker ps
```
*The status of a healthy Elasticsearch component should look as follows:*
```
91220e3285dd docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.11.3 "/bin/tini -- /usr/l…" 11 hours ago Up 11 hours (healthy) 9300/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9200->9200/tcp, :::9200->9200/tcp ragflow-es-01
```
2. Follow [this document](./guides/run_health_check.md) to check the health status of the Elasticsearch service.
:::danger IMPORTANT
The status of a Docker container status does not necessarily reflect the status of the service. You may find that your services are unhealthy even when the corresponding Docker containers are up running. Possible reasons for this include network failures, incorrect port numbers, or DNS issues.
:::
3. If your container keeps restarting, ensure `vm.max_map_count` >= 262144 as per [this README](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow?tab=readme-ov-file#-start-up-the-server). Updating the `vm.max_map_count` value in **/etc/sysctl.conf** is required, if you wish to keep your change permanent. Note that this configuration works only for Linux.
---
### Can't start ES container and get `Elasticsearch did not exit normally`
This is because you forgot to update the `vm.max_map_count` value in **/etc/sysctl.conf** and your change to this value was reset after a system reboot.
---
### `{"data":null,"code":100,"message":"<NotFound '404: Not Found'>"}`
Your IP address or port number may be incorrect. If you are using the default configurations, enter `http://<IP_OF_YOUR_MACHINE>` (**NOT 9380, AND NO PORT NUMBER REQUIRED!**) in your browser. This should work.
---
### `Ollama - Mistral instance running at 127.0.0.1:11434 but cannot add Ollama as model in RagFlow`
A correct Ollama IP address and port is crucial to adding models to Ollama:
- If you are on demo.ragflow.io, ensure that the server hosting Ollama has a publicly accessible IP address. Note that 127.0.0.1 is not a publicly accessible IP address.
- If you deploy RAGFlow locally, ensure that Ollama and RAGFlow are in the same LAN and can communicate with each other.
See [Deploy a local LLM](./guides/models/deploy_local_llm.mdx) for more information.
---
### Do you offer examples of using DeepDoc to parse PDF or other files?
Yes, we do. See the Python files under the **rag/app** folder.
---
### `FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory`
1. Check the status of the MinIO Docker container:
```bash
$ docker ps
```
*The status of a healthy Elasticsearch component should look as follows:*
```bash
cd29bcb254bc quay.io/minio/minio:RELEASE.2023-12-20T01-00-02Z "/usr/bin/docker-ent…" 2 weeks ago Up 11 hours 0.0.0.0:9001->9001/tcp, :::9001->9001/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9000->9000/tcp, :::9000->9000/tcp ragflow-minio
```
2. Follow [this document](./guides/run_health_check.md) to check the health status of the Elasticsearch service.
:::danger IMPORTANT
The status of a Docker container status does not necessarily reflect the status of the service. You may find that your services are unhealthy even when the corresponding Docker containers are up running. Possible reasons for this include network failures, incorrect port numbers, or DNS issues.
:::
---
## Usage
---
### How to run RAGFlow with a locally deployed LLM?
You can use Ollama or Xinference to deploy local LLM. See [here](./guides/models/deploy_local_llm.mdx) for more information.
---
### How to add an LLM that is not supported?
If your model is not currently supported but has APIs compatible with those of OpenAI, click **OpenAI-API-Compatible** on the **Model providers** page to configure your model:

---
### How to integrate RAGFlow with Ollama?
- If RAGFlow is locally deployed, ensure that your RAGFlow and Ollama are in the same LAN.
- If you are using our online demo, ensure that the IP address of your Ollama server is public and accessible.
See [here](./guides/models/deploy_local_llm.mdx) for more information.
---
### How to change the file size limit?
For a locally deployed RAGFlow: the total file size limit per upload is 1GB, with a batch upload limit of 32 files. There is no cap on the total number of files per account. To update this 1GB file size limit:
- In **docker/.env**, upcomment `# MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH=1073741824`, adjust the value as needed, and note that `1073741824` represents 1GB in bytes.
- If you update the value of `MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH` in **docker/.env**, ensure that you update `client_max_body_size` in **nginx/nginx.conf** accordingly.
:::tip NOTE
It is not recommended to manually change the 32-file batch upload limit. However, if you use RAGFlow's HTTP API or Python SDK to upload files, the 32-file batch upload limit is automatically removed.
:::
---
### `Error: Range of input length should be [1, 30000]`
This error occurs because there are too many chunks matching your search criteria. Try reducing the **TopN** and increasing **Similarity threshold** to fix this issue:
1. Click **Chat** in the middle top of the page.
2. Right-click the desired conversation > **Edit** > **Prompt engine**
3. Reduce the **TopN** and/or raise **Similarity threshold**.
4. Click **OK** to confirm your changes.

---
### How to get an API key for integration with third-party applications?
See [Acquire a RAGFlow API key](./develop/acquire_ragflow_api_key.md).
---
### How to upgrade RAGFlow?
See [Upgrade RAGFlow](./guides/upgrade_ragflow.mdx) for more information.
---
### How to switch the document engine to Infinity?
To switch your document engine from Elasticsearch to [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity):
1. Stop all running containers:
```bash
$ docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml down -v
```
:::caution WARNING
`-v` will delete all Docker container volumes, and the existing data will be cleared.
:::
2. In **docker/.env**, set `DOC_ENGINE=${DOC_ENGINE:-infinity}`
3. Restart your Docker image:
```bash
$ docker compose -f docker-compose.yml up -d
```
---
### Where are my uploaded files stored in RAGFlow's image?
All uploaded files are stored in Minio, RAGFlow's object storage solution. For instance, if you upload your file directly to a knowledge base, it is located at `<knowledgebase_id>/filename`.
---
release_notes.md
---
sidebar_position: 2
slug: /release_notes
---
# Releases
Key features, improvements and bug fixes in the latest releases.
:::info
Each RAGFlow release is available in two editions:
- **Slim edition**: excludes built-in embedding models and is identified by a **-slim** suffix added to the version name. Example: `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0-slim`
- **Full edition**: includes built-in embedding models and has no suffix added to the version name. Example: `infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0`
:::
## v0.18.0
Released on April 23, 2025.
### Compatibility changes
From this release onwards, built-in rerank models have been removed because they have minimal impact on retrieval rates but significantly increase retrieval time.
### New features
- MCP server: enables access to RAGFlow's knowledge bases via MCP.
- DeepDoc supports adopting VLM model as a processing pipeline during document layout recognition, enabling in-depth analysis of images in PDF and DOCX files.
- OpenAI-compatible APIs: Agents can be called via OpenAI-compatible APIs.
- User registration control: administrators can enable or disable user registration through an environment variable.
- Team collaboration: Agents can be shared with team members.
- Agent version control: all updates are continuously logged and can be rolled back to a previous version via export.
### Improvements
- Enhanced answer referencing: Citation accuracy in generated responses is improved.
- Enhanced question-answering experience: users can now manually stop streaming output during a conversation.
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Set page rank](./guides/dataset/set_page_rank.md)
- [Enable RAPTOR](./guides/dataset/enable_raptor.md)
- [Set variables for your chat assistant](./guides/chat/set_chat_variables.md)
- [Launch RAGFlow MCP server](./develop/mcp/launch_mcp_server.md)
## v0.17.2
Released on March 13, 2025.
### Compatibility changes
- Removes the **Max_tokens** setting from **Chat configuration**.
- Removes the **Max_tokens** setting from **Generate**, **Rewrite**, **Categorize**, **Keyword** agent components.
From this release onwards, if you still see RAGFlow's responses being cut short or truncated, check the **Max_tokens** setting of your model provider.
### Improvements
- Adds OpenAI-compatible APIs.
- Introduces a German user interface.
- Accelerates knowledge graph extraction.
- Enables Tavily-based web search in the **Retrieval** agent component.
- Adds Tongyi-Qianwen QwQ models (OpenAI-compatible).
- Supports CSV files in the **General** chunking method.
### Fixed issues
- Unable to add models via Ollama/Xinference, an issue introduced in v0.17.1.
### Related APIs
#### HTTP APIs
- [Create chat completion](./references/http_api_reference.md#openai-compatible-api)
#### Python APIs
- [Create chat completion](./references/python_api_reference.md#openai-compatible-api)
## v0.17.1
Released on March 11, 2025.
### Improvements
- Improves English tokenization quality.
- Improves the table extraction logic in Markdown document parsing.
- Updates SiliconFlow's model list.
- Supports parsing XLS files (Excel 97-2003) with improved corresponding error handling.
- Supports Huggingface rerank models.
- Enables relative time expressions ("now", "yesterday", "last week", "next year", and more) in chat assistant and the **Rewrite** agent component.
### Fixed issues
- A repetitive knowledge graph extraction issue.
- Issues with API calling.
- Options in the **PDF parser**, aka **Document parser**, dropdown are missing.
- A Tavily web search issue.
- Unable to preview diagrams or images in an AI chat.
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Use tag set](./guides/dataset/use_tag_sets.md)
## v0.17.0
Released on March 3, 2025.
### New features
- AI chat: Implements Deep Research for agentic reasoning. To activate this, enable the **Reasoning** toggle under the **Prompt engine** tab of your chat assistant dialogue.
- AI chat: Leverages Tavily-based web search to enhance contexts in agentic reasoning. To activate this, enter the correct Tavily API key under the **Assistant settings** tab of your chat assistant dialogue.
- AI chat: Supports starting a chat without specifying knowledge bases.
- AI chat: HTML files can also be previewed and referenced, in addition to PDF files.
- Dataset: Adds a **PDF parser**, aka **Document parser**, dropdown menu to dataset configurations. This includes a DeepDoc model option, which is time-consuming, a much faster **naive** option (plain text), which skips DLA (Document Layout Analysis), OCR (Optical Character Recognition), and TSR (Table Structure Recognition) tasks, and several currently *experimental* large model options.
- Agent component: **(x)** or a forward slash `/` can be used to insert available keys (variables) in the system prompt field of the **Generate** or **Template** component.
- Object storage: Supports using Aliyun OSS (Object Storage Service) as a file storage option.
- Models: Updates the supported model list for Tongyi-Qianwen (Qwen), adding DeepSeek-specific models; adds ModelScope as a model provider.
- APIs: Document metadata can be updated through an API.
The following diagram illustrates the workflow of RAGFlow's Deep Research:

The following is a screenshot of a conversation that integrates Deep Research:

### Related APIs
#### HTTP APIs
Adds a body parameter `"meta_fields"` to the [Update document](./references/http_api_reference.md#update-document) method.
#### Python APIs
Adds a key option `"meta_fields"` to the [Update document](./references/python_api_reference.md#update-document) method.
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Run retrieval test](./guides/dataset/run_retrieval_test.md)
## v0.16.0
Released on February 6, 2025.
### New features
- Supports DeepSeek R1 and DeepSeek V3.
- GraphRAG refactor: Knowledge graph is dynamically built on an entire knowledge base (dataset) rather than on an individual file, and automatically updated when a newly uploaded file starts parsing. See [here](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/construct_knowledge_graph).
- Adds an **Iteration** agent component and a **Research report generator** agent template. See [here](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/iteration.mdx).
- New UI language: Portuguese.
- Allows setting metadata for a specific file in a knowledge base to enhance AI-powered chats. See [here](./guides/dataset/set_metadata.md).
- Upgrades RAGFlow's document engine [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) to v0.6.0.dev3.
- Supports GPU acceleration for DeepDoc (see [docker-compose-gpu.yml](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/docker-compose-gpu.yml)).
- Supports creating and referencing a **Tag** knowledge base as a key milestone towards bridging the semantic gap between query and response.
:::danger IMPORTANT
The **Tag knowledge base** feature is *unavailable* on the [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) document engine.
:::
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Construct knowledge graph](./guides/dataset/construct_knowledge_graph.md)
- [Set metadata](./guides/dataset/set_metadata.md)
- [Begin component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/begin.mdx)
- [Generate component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/generate.mdx)
- [Interact component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/interact.mdx)
- [Retrieval component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/retrieval.mdx)
- [Categorize component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/categorize.mdx)
- [Keyword component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/keyword.mdx)
- [Message component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/message.mdx)
- [Rewrite component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/rewrite.mdx)
- [Switch component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/switch.mdx)
- [Concentrator component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/concentrator.mdx)
- [Template component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/template.mdx)
- [Iteration component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/iteration.mdx)
- [Note component](./guides/agent/agent_component_reference/note.mdx)
## v0.15.1
Released on December 25, 2024.
### Upgrades
- Upgrades RAGFlow's document engine [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) to v0.5.2.
- Enhances the log display of document parsing status.
### Fixed issues
This release fixes the following issues:
- The `SCORE not found` and `position_int` errors returned by [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity).
- Once an embedding model in a specific knowledge base is changed, embedding models in other knowledge bases can no longer be changed.
- Slow response in question-answering and AI search due to repetitive loading of the embedding model.
- Fails to parse documents with RAPTOR.
- Using the **Table** parsing method results in information loss.
- Miscellaneous API issues.
### Related APIs
#### HTTP APIs
Adds an optional parameter `"user_id"` to the following APIs:
- [Create session with chat assistant](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#create-session-with-chat-assistant)
- [Update chat assistant's session](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#update-chat-assistants-session)
- [List chat assistant's sessions](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#list-chat-assistants-sessions)
- [Create session with agent](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#create-session-with-agent)
- [Converse with chat assistant](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#converse-with-chat-assistant)
- [Converse with agent](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#converse-with-agent)
- [List agent sessions](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#list-agent-sessions)
## v0.15.0
Released on December 18, 2024.
### New features
- Introduces additional Agent-specific APIs.
- Supports using page rank score to improve retrieval performance when searching across multiple knowledge bases.
- Offers an iframe in Chat and Agent to facilitate the integration of RAGFlow into your webpage.
- Adds a Helm chart for deploying RAGFlow on Kubernetes.
- Supports importing or exporting an agent in JSON format.
- Supports step run for Agent components/tools.
- Adds a new UI language: Japanese.
- Supports resuming GraphRAG and RAPTOR from a failure, enhancing task management resilience.
- Adds more Mistral models.
- Adds a dark mode to the UI, allowing users to toggle between light and dark themes.
### Improvements
- Upgrades the Document Layout Analysis model in DeepDoc.
- Significantly enhances the retrieval performance when using [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) as document engine.
### Related APIs
#### HTTP APIs
- [List agent sessions](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#list-agent-sessions)
- [List agents](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#list-agents)
#### Python APIs
- [List agent sessions](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/python_api_reference#list-agent-sessions)
- [List agents](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/python_api_reference#list-agents)
## v0.14.1
Released on November 29, 2024.
### Improvements
Adds [Infinity's configuration file](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/infinity_conf.toml) to facilitate integration and customization of [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) as a document engine. From this release onwards, updates to Infinity's configuration can be made directly within RAGFlow and will take effect immediately after restarting RAGFlow using `docker compose`. [#3715](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/pull/3715)
### Fixed issues
This release fixes the following issues:
- Unable to display or edit content of a chunk after clicking it.
- A `'Not found'` error in Elasticsearch.
- Chinese text becoming garbled during parsing.
- A compatibility issue with Polars.
- A compatibility issue between Infinity and GraphRAG.
## v0.14.0
Released on November 26, 2024.
### New features
- Supports [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) or Elasticsearch (default) as document engine for vector storage and full-text indexing. [#2894](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/pull/2894)
- Enhances user experience by adding more variables to the Agent and implementing auto-saving.
- Adds a three-step translation agent template, inspired by [Andrew Ng's translation agent](https://github.com/andrewyng/translation-agent).
- Adds an SEO-optimized blog writing agent template.
- Provides HTTP and Python APIs for conversing with an agent.
- Supports the use of English synonyms during retrieval processes.
- Optimizes term weight calculations, reducing the retrieval time by 50%.
- Improves task executor monitoring with additional performance indicators.
- Replaces Redis with Valkey.
- Adds three new UI languages (*contributed by the community*): Indonesian, Spanish, and Vietnamese.
### Compatibility changes
From this release onwards, **service_config.yaml.template** replaces **service_config.yaml** for configuring backend services. Upon Docker container startup, the environment variables defined in this template file are automatically populated and a **service_config.yaml** is auto-generated from it. [#3341](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/pull/3341)
This approach eliminates the need to manually update **service_config.yaml** after making changes to **.env**, facilitating dynamic environment configurations.
:::danger IMPORTANT
Ensure that you [upgrade **both** your code **and** Docker image to this release](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/upgrade_ragflow#upgrade-ragflow-to-the-most-recent-officially-published-release) before trying this new approach.
:::
### Related APIs
#### HTTP APIs
- [Create session with agent](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#create-session-with-agent)
- [Converse with agent](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#converse-with-agent)
#### Python APIs
- [Create session with agent](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/python_api_reference#create-session-with-agent)
- [Converse with agent](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/python_api_reference#create-session-with-agent)
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Configurations](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/configurations)
- [Manage team members](./guides/team/manage_team_members.md)
- [Run health check on RAGFlow's dependencies](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/run_health_check)
## v0.13.0
Released on October 31, 2024.
### New features
- Adds the team management functionality for all users.
- Updates the Agent UI to improve usability.
- Adds support for Markdown chunking in the **General** chunking method.
- Introduces an **invoke** tool within the Agent UI.
- Integrates support for Dify's knowledge base API.
- Adds support for GLM4-9B and Yi-Lightning models.
- Introduces HTTP and Python APIs for dataset management, file management within dataset, and chat assistant management.
:::tip NOTE
To download RAGFlow's Python SDK:
```bash
pip install ragflow-sdk==0.13.0
```
:::
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Acquire a RAGFlow API key](./develop/acquire_ragflow_api_key.md)
- [HTTP API Reference](./references/http_api_reference.md)
- [Python API Reference](./references/python_api_reference.md)
## v0.12.0
Released on September 30, 2024.
### New features
- Offers slim editions of RAGFlow's Docker images, which do not include built-in BGE/BCE embedding or reranking models.
- Improves the results of multi-round dialogues.
- Enables users to remove added LLM vendors.
- Adds support for **OpenTTS** and **SparkTTS** models.
- Implements an **Excel to HTML** toggle in the **General** chunking method, allowing users to parse a spreadsheet into either HTML tables or key-value pairs by row.
- Adds agent tools **YahooFinance** and **Jin10**.
- Adds an investment advisor agent template.
### Compatibility changes
From this release onwards, RAGFlow offers slim editions of its Docker images to improve the experience for users with limited Internet access. A slim edition of RAGFlow's Docker image does not include built-in BGE/BCE embedding models and has a size of about 1GB; a full edition of RAGFlow is approximately 9GB and includes both built-in embedding models and embedding models that will be downloaded once you select them in the RAGFlow UI.
The default Docker image edition is `nightly-slim`. The following list clarifies the differences between various editions:
- `nightly-slim`: The slim edition of the most recent tested Docker image.
- `v0.12.0-slim`: The slim edition of the most recent **officially released** Docker image.
- `nightly`: The full edition of the most recent tested Docker image.
- `v0.12.0`: The full edition of the most recent **officially released** Docker image.
See [Upgrade RAGFlow](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/upgrade_ragflow) for instructions on upgrading.
### Documentation
#### Added documents
- [Upgrade RAGFlow](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/upgrade_ragflow)
## v0.11.0
Released on September 14, 2024.
### New features
- Introduces an AI search interface within the RAGFlow UI.
- Supports audio output via **FishAudio** or **Tongyi Qwen TTS**.
- Allows the use of Postgres for metadata storage, in addition to MySQL.
- Supports object storage options with S3 or Azure Blob.
- Supports model vendors: **Anthropic**, **Voyage AI**, and **Google Cloud**.
- Supports the use of **Tencent Cloud ASR** for audio content recognition.
- Adds finance-specific agent components: **WenCai**, **AkShare**, **YahooFinance**, and **TuShare**.
- Adds a medical consultant agent template.
- Supports running retrieval benchmarking on the following datasets:
- [ms_marco_v1.1](https://huggingface.co/datasets/microsoft/ms_marco)
- [trivia_qa](https://huggingface.co/datasets/mandarjoshi/trivia_qa)
- [miracl](https://huggingface.co/datasets/miracl/miracl)
## v0.10.0
Released on August 26, 2024.
### New features
- Introduces a text-to-SQL template in the Agent UI.
- Implements Agent APIs.
- Incorporates monitoring for the task executor.
- Introduces Agent tools **GitHub**, **DeepL**, **BaiduFanyi**, **QWeather**, and **GoogleScholar**.
- Supports chunking of EML files.
- Supports more LLMs or model services: **GPT-4o-mini**, **PerfXCloud**, **TogetherAI**, **Upstage**, **Novita AI**, **01.AI**, **SiliconFlow**, **PPIO**, **XunFei Spark**, **Baidu Yiyan**, and **Tencent Hunyuan**.
## v0.9.0
Released on August 6, 2024.
### New features
- Supports GraphRAG as a chunking method.
- Introduces Agent component **Keyword** and search tools, including **Baidu**, **DuckDuckGo**, **PubMed**, **Wikipedia**, **Bing**, and **Google**.
- Supports speech-to-text recognition for audio files.
- Supports model vendors **Gemini** and **Groq**.
- Supports inference frameworks, engines, and services including **LM studio**, **OpenRouter**, **LocalAI**, and **Nvidia API**.
- Supports using reranker models in Xinference.
## v0.8.0
Released on July 8, 2024.
### New features
- Supports Agentic RAG, enabling graph-based workflow construction for RAG and agents.
- Supports model vendors **Mistral**, **MiniMax**, **Bedrock**, and **Azure OpenAI**.
- Supports DOCX files in the MANUAL chunking method.
- Supports DOCX, MD, and PDF files in the Q&A chunking method.
## v0.7.0
Released on May 31, 2024.
### New features
- Supports the use of reranker models.
- Integrates reranker and embedding models: [BCE](https://github.com/netease-youdao/BCEmbedding), [BGE](https://github.com/FlagOpen/FlagEmbedding), and [Jina](https://jina.ai/embeddings/).
- Supports LLMs Baichuan and VolcanoArk.
- Implements [RAPTOR](https://arxiv.org/html/2401.18059v1) for improved text retrieval.
- Supports HTML files in the GENERAL chunking method.
- Provides HTTP and Python APIs for deleting documents by ID.
- Supports ARM64 platforms.
:::danger IMPORTANT
While we also test RAGFlow on ARM64 platforms, we do not maintain RAGFlow Docker images for ARM.
If you are on an ARM platform, follow [this guide](./develop/build_docker_image.mdx) to build a RAGFlow Docker image.
:::
### Related APIs
#### HTTP API
- [Delete documents](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#delete-documents)
#### Python API
- [Delete documents](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/python_api_reference#delete-documents)
## v0.6.0
Released on May 21, 2024.
### New features
- Supports streaming output.
- Provides HTTP and Python APIs for retrieving document chunks.
- Supports monitoring of system components, including Elasticsearch, MySQL, Redis, and MinIO.
- Supports disabling **Layout Recognition** in the GENERAL chunking method to reduce file chunking time.
### Related APIs
#### HTTP API
- [Retrieve chunks](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/http_api_reference#retrieve-chunks)
#### Python API
- [Retrieve chunks](https://ragflow.io/docs/dev/python_api_reference#retrieve-chunks)
## v0.5.0
Released on May 8, 2024.
### New features
- Supports LLM DeepSeek.
develop_category_.json
{
"label": "Developers",
"position": 4,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Guides for hardcore developers"
}
}
develop\acquire_ragflow_api_key.md
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /acquire_ragflow_api_key
---
# Acquire RAGFlow API key
An API key is required for the RAGFlow server to authenticate your HTTP/Python or MCP requests. This documents provides instructions on obtaining a RAGFlow API key.
1. Click your avatar in the top right corner of the RAGFlow UI to access the configuration page.
2. Click **API** to switch to the **API** page.
3. Obtain a RAGFlow API key:

:::tip NOTE
See the [RAGFlow HTTP API reference](../references/http_api_reference.md) or the [RAGFlow Python API reference](../references/python_api_reference.md) for a complete reference of RAGFlow's HTTP or Python APIs.
:::
develop\launch_ragflow_from_source.md
---
sidebar_position: 2
slug: /launch_ragflow_from_source
---
# Launch service from source
A guide explaining how to set up a RAGFlow service from its source code. By following this guide, you'll be able to debug using the source code.
## Target audience
Developers who have added new features or modified existing code and wish to debug using the source code, *provided that* their machine has the target deployment environment set up.
## Prerequisites
- CPU ≥ 4 cores
- RAM ≥ 16 GB
- Disk ≥ 50 GB
- Docker ≥ 24.0.0 & Docker Compose ≥ v2.26.1
:::tip NOTE
If you have not installed Docker on your local machine (Windows, Mac, or Linux), see the [Install Docker Engine](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/) guide.
:::
## Launch a service from source
To launch a RAGFlow service from source code:
### Clone the RAGFlow repository
```bash
git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
cd ragflow/
```
### Install Python dependencies
1. Install uv:
```bash
pipx install uv
```
2. Install Python dependencies:
- slim:
```bash
uv sync --python 3.10 # install RAGFlow dependent python modules
```
- full:
```bash
uv sync --python 3.10 --all-extras # install RAGFlow dependent python modules
```
*A virtual environment named `.venv` is created, and all Python dependencies are installed into the new environment.*
### Launch third-party services
The following command launches the 'base' services (MinIO, Elasticsearch, Redis, and MySQL) using Docker Compose:
```bash
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose-base.yml up -d
```
### Update `host` and `port` Settings for Third-party Services
1. Add the following line to `/etc/hosts` to resolve all hosts specified in **docker/service_conf.yaml.template** to `127.0.0.1`:
```
127.0.0.1 es01 infinity mysql minio redis
```
2. In **docker/service_conf.yaml.template**, update mysql port to `5455` and es port to `1200`, as specified in **docker/.env**.
### Launch the RAGFlow backend service
1. Comment out the `nginx` line in **docker/entrypoint.sh**.
```
# /usr/sbin/nginx
```
2. Activate the Python virtual environment:
```bash
source .venv/bin/activate
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)
```
3. **Optional:** If you cannot access HuggingFace, set the HF_ENDPOINT environment variable to use a mirror site:
```bash
export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
```
4. Check the configuration in **conf/service_conf.yaml**, ensuring all hosts and ports are correctly set.
5. Run the **entrypoint.sh** script to launch the backend service:
```shell
JEMALLOC_PATH=$(pkg-config --variable=libdir jemalloc)/libjemalloc.so;
LD_PRELOAD=$JEMALLOC_PATH python rag/svr/task_executor.py 1;
```
```shell
python api/ragflow_server.py;
```
### Launch the RAGFlow frontend service
1. Navigate to the `web` directory and install the frontend dependencies:
```bash
cd web
npm install
```
2. Update `proxy.target` in **.umirc.ts** to `http://127.0.0.1:9380`:
```bash
vim .umirc.ts
```
3. Start up the RAGFlow frontend service:
```bash
npm run dev
```
*The following message appears, showing the IP address and port number of your frontend service:*
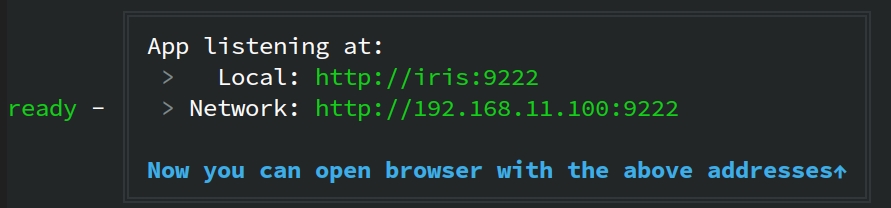
### Access the RAGFlow service
In your web browser, enter `http://127.0.0.1:<PORT>/`, ensuring the port number matches that shown in the screenshot above.
### Stop the RAGFlow service when the development is done
1. Stop the RAGFlow frontend service:
```bash
pkill npm
```
2. Stop the RAGFlow backend service:
```bash
pkill -f "docker/entrypoint.sh"
```
develop\mcp_category_.json
{
"label": "MCP",
"position": 4,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Guides and references on accessing RAGFlow's knowledge bases via MCP."
}
}
develop\mcp\mcp_client_example.md
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /mcp_client
---
# RAGFlow MCP client example
We provide a *prototype* MCP client example for testing [here](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/mcp/client/client.py).
:::danger IMPORTANT
If your MCP server is running in host mode, include your acquired API key in your client's `headers` as shown below:
```python
async with sse_client("http://localhost:9382/sse", headers={"api_key": "YOUR_KEY_HERE"}) as streams:
# Rest of your code...
```
:::
develop\mcp\mcp_tools.md
---
sidebar_position: 2
slug: /mcp_tools
---
# RAGFlow MCP tools
The MCP server currently offers a specialized tool to assist users in searching for relevant information powered by RAGFlow DeepDoc technology:
- **retrieve**: Fetches relevant chunks from specified `dataset_ids` and optional `document_ids` using the RAGFlow retrieve interface, based on a given question. Details of all available datasets, namely, `id` and `description`, are provided within the tool description for each individual dataset.
For more information, see our Python implementation of the [MCP server](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/mcp/server/server.py).
guides_category_.json
{
"label": "Guides",
"position": 3,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Guides for RAGFlow users and developers."
}
}
guides\manage_files.md
---
sidebar_position: 6
slug: /manage_files
---
# Files
Knowledge base, hallucination-free chat, and file management are the three pillars of RAGFlow. RAGFlow's file management allows you to upload files individually or in bulk. You can then link an uploaded file to multiple target knowledge bases. This guide showcases some basic usages of the file management feature.
:::info IMPORTANT
Compared to uploading files directly to various knowledge bases, uploading them to RAGFlow's file management and then linking them to different knowledge bases is *not* an unnecessary step, particularly when you want to delete some parsed files or an entire knowledge base but retain the original files.
:::
## Create folder
RAGFlow's file management allows you to establish your file system with nested folder structures. To create a folder in the root directory of RAGFlow:

:::caution NOTE
Each knowledge base in RAGFlow has a corresponding folder under the **root/.knowledgebase** directory. You are not allowed to create a subfolder within it.
:::
## Upload file
RAGFlow's file management supports file uploads from your local machine, allowing both individual and bulk uploads:


## Preview file
RAGFlow's file management supports previewing files in the following formats:
- Documents (PDF, DOCS)
- Tables (XLSX)
- Pictures (JPEG, JPG, PNG, TIF, GIF)

## Link file to knowledge bases
RAGFlow's file management allows you to *link* an uploaded file to multiple knowledge bases, creating a file reference in each target knowledge base. Therefore, deleting a file in your file management will AUTOMATICALLY REMOVE all related file references across the knowledge bases.

You can link your file to one knowledge base or multiple knowledge bases at one time:

## Move file to a specific folder

## Search files or folders
**File Management** only supports file name and folder name filtering in the current directory (files or folders in the child directory will not be retrieved).

## Rename file or folder
RAGFlow's file management allows you to rename a file or folder:

## Delete files or folders
RAGFlow's file management allows you to delete files or folders individually or in bulk.
To delete a file or folder:

To bulk delete files or folders:

> - You are not allowed to delete the **root/.knowledgebase** folder.
> - Deleting files that have been linked to knowledge bases will **AUTOMATICALLY REMOVE** all associated file references across the knowledge bases.
## Download uploaded file
RAGFlow's file management allows you to download an uploaded file:

> As of RAGFlow v0.18.0, bulk download is not supported, nor can you download an entire folder.
guides\run_health_check.md
---
sidebar_position: 8
slug: /run_health_check
---
# Monitoring
Double-check the health status of RAGFlow's dependencies.
---
The operation of RAGFlow depends on four services:
- **Elasticsearch** (default) or [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) as the document engine
- **MySQL**
- **Redis**
- **MinIO** for object storage
If an exception or error occurs related to any of the above services, such as `Exception: Can't connect to ES cluster`, refer to this document to check their health status.
You can also click you avatar in the top right corner of the page **>** System to view the visualized health status of RAGFlow's core services. The following screenshot shows that all services are 'green' (running healthily). The task executor displays the *cumulative* number of completed and failed document parsing tasks from the past 30 minutes:
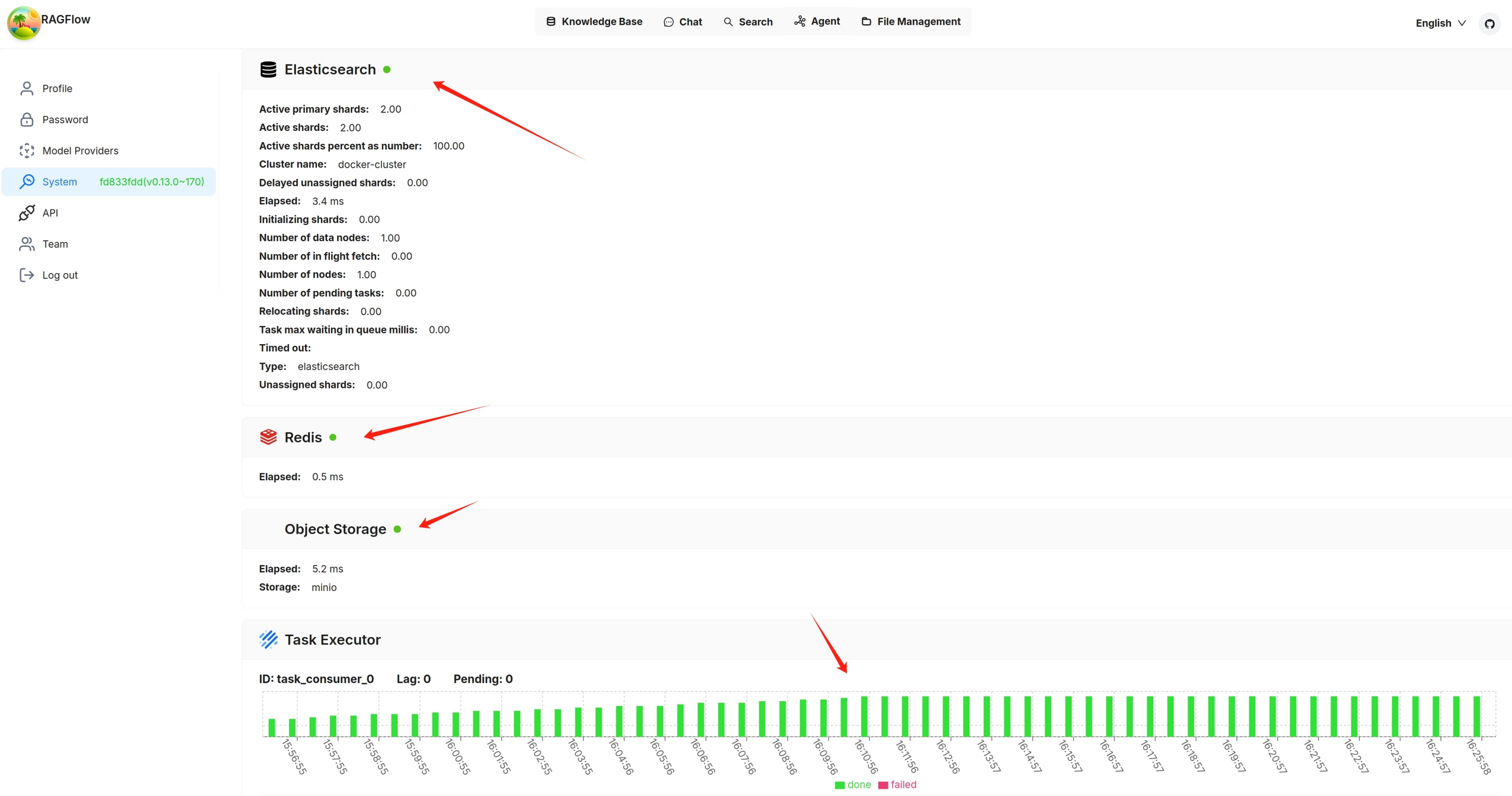
Services with a yellow or red light are not running properly. The following is a screenshot of the system page after running `docker stop ragflow-es-10`:

You can click on a specific 30-second time interval to view the details of completed and failed tasks:


guides\upgrade_ragflow.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 11
slug: /upgrade_ragflow
---
# Upgrading
import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
Upgrade RAGFlow to `nightly-slim`/`nightly` or the latest, published release.
:::info NOTE
Upgrading RAGFlow in itself will *not* remove your uploaded/historical data. However, be aware that `docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml down -v` will remove Docker container volumes, resulting in data loss.
:::
## Upgrade RAGFlow to `nightly-slim`/`nightly`, the most recent, tested Docker image
`nightly-slim` refers to the RAGFlow Docker image *without* embedding models, while `nightly` refers to the RAGFlow Docker image with embedding models. For details on their differences, see [ragflow/docker/.env](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/docker/.env).
To upgrade RAGFlow, you must upgrade **both** your code **and** your Docker image:
1. Clone the repo
```bash
git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
```
2. Update **ragflow/docker/.env**:
<Tabs
defaultValue="nightly-slim"
values={[
{label: 'nightly-slim', value: 'nightly-slim'},
{label: 'nightly', value: 'nightly'},
]}>
<TabItem value="nightly-slim">
```bash
RAGFLOW_IMAGE=infiniflow/ragflow:nightly-slim
```
</TabItem>
<TabItem value="nightly">
```bash
RAGFLOW_IMAGE=infiniflow/ragflow:nightly
```
</TabItem>
</Tabs>
3. Update RAGFlow image and restart RAGFlow:
```bash
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml pull
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -d
```
## Upgrade RAGFlow to the most recent, officially published release
To upgrade RAGFlow, you must upgrade **both** your code **and** your Docker image:
1. Clone the repo
```bash
git clone https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow.git
```
2. Switch to the latest, officially published release, e.g., `v0.18.0`:
```bash
git checkout -f v0.18.0
```
3. Update **ragflow/docker/.env** as follows:
```bash
RAGFLOW_IMAGE=infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0
```
4. Update the RAGFlow image and restart RAGFlow:
```bash
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml pull
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up -d
```
## Frequently asked questions
### Upgrade RAGFlow in an offline environment (without Internet access)
1. From an environment with Internet access, pull the required Docker image.
2. Save the Docker image to a **.tar** file.
```bash
docker save -o ragflow.v0.18.0.tar infiniflow/ragflow:v0.18.0
```
3. Copy the **.tar** file to the target server.
4. Load the **.tar** file into Docker:
```bash
docker load -i ragflow.v0.18.0.tar
```
guides\agent_category_.json
{
"label": "Agents",
"position": 3,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "RAGFlow v0.8.0 introduces an agent mechanism, featuring a no-code workflow editor on the front end and a comprehensive graph-based task orchestration framework on the backend."
}
}
guides\agent\agent_introduction.md
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /agent_introduction
---
# Introduction to agents
Key concepts, basic operations, a quick view of the agent editor.
---
## Key concepts
Agents and RAG are complementary techniques, each enhancing the other’s capabilities in business applications. RAGFlow v0.8.0 introduces an agent mechanism, featuring a no-code workflow editor on the front end and a comprehensive graph-based task orchestration framework on the back end. This mechanism is built on top of RAGFlow's existing RAG solutions and aims to orchestrate search technologies such as query intent classification, conversation leading, and query rewriting to:
- Provide higher retrievals and,
- Accommodate more complex scenarios.
## Create an agent
:::tip NOTE
Before proceeding, ensure that:
1. You have properly set the LLM to use. See the guides on [Configure your API key](../models/llm_api_key_setup.md) or [Deploy a local LLM](../models/deploy_local_llm.mdx) for more information.
2. You have a knowledge base configured and the corresponding files properly parsed. See the guide on [Configure a knowledge base](../dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md) for more information.
:::
Click the **Agent** tab in the middle top of the page to show the **Agent** page. As shown in the screenshot below, the cards on this page represent the created agents, which you can continue to edit.

We also provide templates catered to different business scenarios. You can either generate your agent from one of our agent templates or create one from scratch:
1. Click **+ Create agent** to show the **agent template** page:

2. To create an agent from scratch, click the **Blank** card. Alternatively, to create an agent from one of our templates, hover over the desired card, such as **General-purpose chatbot**, click **Use this template**, name your agent in the pop-up dialogue, and click **OK** to confirm.
*You are now taken to the **no-code workflow editor** page. The left panel lists the components (operators): Above the dividing line are the RAG-specific components; below the line are tools. We are still working to expand the component list.*

3. General speaking, now you can do the following:
- Drag and drop a desired component to your workflow,
- Select the knowledge base to use,
- Update settings of specific components,
- Update LLM settings
- Sets the input and output for a specific component, and more.
4. Click **Save** to apply changes to your agent and **Run** to test it.
## Components
Please review the flowing description of the RAG-specific components before you proceed:
| Component | Description |
|----------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **Retrieval** | A component that retrieves information from specified knowledge bases and returns 'Empty response' if no information is found. Ensure the correct knowledge bases are selected. |
| **Generate** | A component that prompts the LLM to generate responses. You must ensure the prompt is set correctly. |
| **Interact** | A component that serves as the interface between human and the bot, receiving user inputs and displaying the agent's responses. |
| **Categorize** | A component that uses the LLM to classify user inputs into predefined categories. Ensure you specify the name, description, and examples for each category, along with the corresponding next component. |
| **Message** | A component that sends out a static message. If multiple messages are supplied, it randomly selects one to send. Ensure its downstream is **Interact**, the interface component. |
| **Rewrite** | A component that rewrites a user query from the **Interact** component, based on the context of previous dialogues. |
| **Keyword** | A component that extracts keywords from a user query, with TopN specifying the number of keywords to extract. |
:::caution NOTE
- Ensure **Rewrite**'s upstream component is **Relevant** and downstream component is **Retrieval**.
- Ensure the downstream component of **Message** is **Interact**.
- The downstream component of **Begin** is always **Interact**.
:::
## Basic operations
| Operation | Description |
|---------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Add a component | Drag and drop the desired component from the left panel onto the canvas. |
| Delete a component | On the canvas, hover over the three dots (...) of the component to display the delete option, then select it to remove the component. |
| Copy a component | On the canvas, hover over the three dots (...) of the component to display the copy option, then select it to make a copy the component. |
| Update component settings | On the canvas, click the desired component to display the component settings. |
guides\agent\embed_agent_into_webpage.md
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /embed_agent_into_webpage
---
# Embed agent into webpage
You can use iframe to embed an agent into a third-party webpage.
:::caution WARNING
If your agent's **Begin** component takes a variable, you *cannot* embed it into a webpage.
:::
1. Before proceeding, you must [acquire an API key](../models/llm_api_key_setup.md); otherwise, an error message would appear.
2. On the **Agent** page, click an intended agent **>** **Edit** to access its editing page.
3. Click **Embed into webpage** on the top right corner of the canvas to show the **iframe** window:

4. Copy the iframe and embed it into a specific location on your webpage.
guides\agent\general_purpose_chatbot.md
---
sidebar_position: 2
slug: /general_purpose_chatbot
---
# Create chatbot
Create a general-purpose chatbot.
---
Chatbot is one of the most common AI scenarios. However, effectively understanding user queries and responding appropriately remains a challenge. RAGFlow's general-purpose chatbot agent is our attempt to tackle this longstanding issue.
This chatbot closely resembles the chatbot introduced in [Start an AI chat](../chat/start_chat.md), but with a key difference - it introduces a reflective mechanism that allows it to improve the retrieval from the target knowledge bases by rewriting the user's query.
This document provides guides on creating such a chatbot using our chatbot template.
## Prerequisites
1. Ensure you have properly set the LLM to use. See the guides on [Configure your API key](../models/llm_api_key_setup.md) or [Deploy a local LLM](../models/deploy_local_llm.mdx) for more information.
2. Ensure you have a knowledge base configured and the corresponding files properly parsed. See the guide on [Configure a knowledge base](../dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md) for more information.
3. Make sure you have read the [Introduction to Agentic RAG](./agent_introduction.md).
## Create a chatbot agent from template
To create a general-purpose chatbot agent using our template:
1. Click the **Agent** tab in the middle top of the page to show the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to show the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the card on **General-purpose chatbot** and click **Use this template**.
*You are now directed to the **no-code workflow editor** page.*

:::tip NOTE
RAGFlow's no-code editor spares you the trouble of coding, making agent development effortless.
:::
## Understand each component in the template
Here’s a breakdown of each component and its role and requirements in the chatbot template:
- **Begin**
- Function: Sets an opening greeting for users.
- Purpose: Establishes a welcoming atmosphere and prepares the user for interaction.
- **Interact**
- Function: Serves as the interface between human and the bot.
- Role: Acts as the downstream component of **Begin**.
- **Retrieval**
- Function: Retrieves information from specified knowledge base(s).
- Requirement: Must have `knowledgebases` set up to function.
- **Relevant**
- Function: Assesses the relevance of the retrieved information from the **Retrieval** component to the user query.
- Process:
- If relevant, it directs the data to the **Generate** component for final response generation.
- Otherwise, it triggers the **Rewrite** component to refine the user query and redo the retrival process.
- **Generate**
- Function: Prompts the LLM to generate responses based on the retrieved information.
- Note: The prompt settings allow you to control the way in which the LLM generates responses. Be sure to review the prompts and make necessary changes.
- **Rewrite**:
- Function: Refines a user query when no relevant information from the knowledge base is retrieved.
- Usage: Often used in conjunction with **Relevant** and **Retrieval** to create a reflective/feedback loop.
## Configure your chatbot agent
1. Click **Begin** to set an opening greeting:

2. Click **Retrieval** to select the right knowledge base(s) and make any necessary adjustments:

3. Click **Generate** to configure the LLM's summarization behavior:
3.1. Confirm the model.
3.2. Review the prompt settings. If there are variables, ensure they match the correct component IDs:

4. Click **Relevant** to review or change its settings:
*You may retain the current settings, but feel free to experiment with changes to understand how the agent operates.*

5. Click **Rewrite** to select a different model for query rewriting or update the maximum loop times for query rewriting:
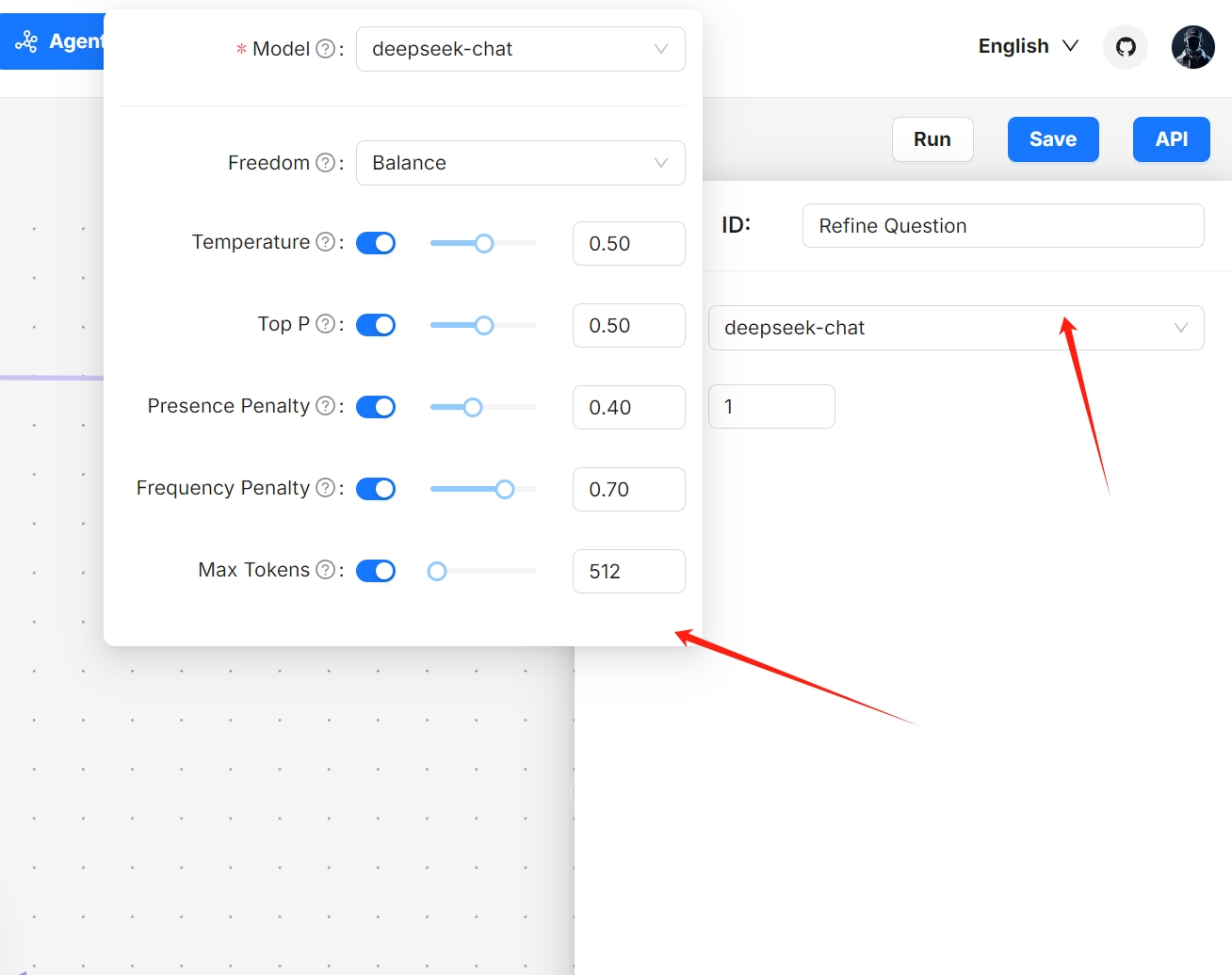

:::danger NOTE
Increasing the maximum loop times may significantly extend the time required to receive the final response.
:::
1. Update your workflow where you see necessary.
2. Click to **Save** to apply your changes.
*Your agent appears as one of the agent cards on the **Agent** page.*
## Test your chatbot agent
1. Find your chatbot agent on the **Agent** page:

2. Experiment with your questions to verify if this chatbot functions as intended:

guides\agent\agent_component_reference_category_.json
{
"label": "Agent Components",
"position": 20,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "A complete reference for RAGFlow's agent components."
}
}
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\begin.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /begin_component
---
# Begin component
The starting component in a workflow.
---
The **Begin** component sets an opening greeting or accepts inputs from the user. It is automatically populated onto the canvas when you create an agent, whether from a template or from scratch (from a blank template). There should be only one **Begin** component in the workflow.
## Scenarios
A **Begin** component is essential in all cases. Every agent includes a **Begin** component, which cannot be deleted.
## Configurations
Click the component to display its **Configuration** window. Here, you can set an opening greeting and the input parameters (global variables) for the agent.
### ID
The ID is the unique identifier for the component within the workflow. Unlike the IDs of other components, the ID of the **Begin** component *cannot* be changed.
### Opening greeting
An opening greeting is the agent's first message to the user. It can be a welcoming remark or an instruction to guide the user forward.
### Global variables
You can set global variables within the **Begin** component, which can be either required or optional. Once established, users will need to provide values for these variables when interacting or chatting with the agent. Click **+ Add variable** to add a global variable, each with the following attributes:
- **Key**: *Required*
The unique variable name.
- **Name**: *Required*
A descriptive name providing additional details about the variable.
For example, if **Key** is set to `lang`, you can set its **Name** to `Target language`.
- **Type**: *Required*
The type of the variable:
- **line**: Accepts a single line of text without line breaks.
- **paragraph**: Accepts multiple lines of text, including line breaks.
- **options**: Requires the user to select a value for this variable from a dropdown menu. And you are required to set *at least* one option for the dropdown menu.
- **file**: Requires the user to upload one or multiple files.
- **integer**: Accepts an integer as input.
- **boolean**: Requires the user to toggle between on and off.
- **Optional**: A toggle indicating whether the variable is optional.
:::tip NOTE
To pass in parameters from a client, call:
- HTTP method [Converse with agent](../../../references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-agent), or
- Python method [Converse with agent](../../../references/python_api_reference.md#converse-with-agent).
:::
:::danger IMPORTANT
- If you set the key type as **file**, ensure the token count of the uploaded file does not exceed your model provider's maximum token limit; otherwise, the plain text in your file will be truncated and incomplete.
- If your agent's **Begin** component takes a variable, you *cannot* embed it into a webpage.
:::
## Examples
As mentioned earlier, the **Begin** component is indispensable for an agent. Still, you can take a look at our three-step interpreter agent template, where the **Begin** component takes two global variables:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Interpreter** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Begin** component to display its **Configuration** window.
## Frequently asked questions
### Is the uploaded file in a knowledge base?
No. Files uploaded to an agent as input are not stored in a knowledge base and hence will not be processed using RAGFlow's built-in OCR, DLR or TSR models, or chunked using RAGFlow's built-in chunking methods.
### How to upload a webpage or file from a URL?
If you set the type of a variable as **file**, your users will be able to upload a file either from their local device or from an accessible URL. For example:

### File size limit for an uploaded file
There is no *specific* file size limit for a file uploaded to an agent. However, note that model providers typically have a default or explicit maximum token setting, which can range from 8196 to 128k: The plain text part of the uploaded file will be passed in as the key value, but if the file's token count exceeds this limit, the string will be truncated and incomplete.
:::tip NOTE
The variables `MAX_CONTENT_LENGTH` in `/docker/.env` and `client_max_body_size` in `/docker/nginx/nginx.conf` set the file size limit for each upload to a knowledge base or **File Management**. These settings DO NOT apply in this scenario.
:::
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\categorize.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 5
slug: /categorize_component
---
# Categorize component
A component that classifies user inputs and applies strategies accordingly.
---
A **Categorize** component is usually the downstream of the **Interact** component.
## Scenarios
A **Categorize** component is essential when you need the LLM to help you identify user intentions and apply appropriate processing strategies.
## Configurations
### Input
The **Categorize** component relies on input variables to specify its data inputs (queries). Click **+ Add variable** in the **Input** section to add the desired input variables. There are two types of input variables: **Reference** and **Text**.
- **Reference**: Uses a component's output or a user input as the data source. You are required to select from the dropdown menu:
- A component ID under **Component Output**, or
- A global variable under **Begin input**, which is defined in the **Begin** component.
- **Text**: Uses fixed text as the query. You are required to enter static text.
### Model
Click the dropdown menu of **Model** to show the model configuration window.
- **Model**: The chat model to use.
- Ensure you set the chat model correctly on the **Model providers** page.
- You can use different models for different components to increase flexibility or improve overall performance.
- **Freedom**: A shortcut to **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty** settings, indicating the freedom level of the model. From **Improvise**, **Precise**, to **Balance**, each preset configuration corresponds to a unique combination of **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**.
This parameter has three options:
- **Improvise**: Produces more creative responses.
- **Precise**: (Default) Produces more conservative responses.
- **Balance**: A middle ground between **Improvise** and **Precise**.
- **Temperature**: The randomness level of the model's output.
Defaults to 0.1.
- Lower values lead to more deterministic and predictable outputs.
- Higher values lead to more creative and varied outputs.
- A temperature of zero results in the same output for the same prompt.
- **Top P**: Nucleus sampling.
- Reduces the likelihood of generating repetitive or unnatural text by setting a threshold *P* and restricting the sampling to tokens with a cumulative probability exceeding *P*.
- Defaults to 0.3.
- **Presence penalty**: Encourages the model to include a more diverse range of tokens in the response.
- A higher **presence penalty** value results in the model being more likely to generate tokens not yet been included in the generated text.
- Defaults to 0.4.
- **Frequency penalty**: Discourages the model from repeating the same words or phrases too frequently in the generated text.
- A higher **frequency penalty** value results in the model being more conservative in its use of repeated tokens.
- Defaults to 0.7.
:::tip NOTE
- It is not necessary to stick with the same model for all components. If a specific model is not performing well for a particular task, consider using a different one.
- If you are uncertain about the mechanism behind **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**, simply choose one of the three options of **Preset configurations**.
:::
### Message window size
An integer specifying the number of previous dialogue rounds to input into the LLM. For example, if it is set to 12, the tokens from the last 12 dialogue rounds will be fed to the LLM. This feature consumes additional tokens.
Defaults to 1.
:::tip IMPORTANT
This feature is used for multi-turn dialogue *only*. If your **Categorize** component is not part of a multi-turn dialogue (i.e., it is not in a loop), leave this field as-is.
:::
### Category name
A **Categorize** component must have at least two categories. This field sets the name of the category. Click **+ Add Item** to include the intended categories.
:::tip NOTE
You will notice that the category name is auto-populated. No worries. Each category is assigned a random name upon creation. Feel free to change it to a name that is understandable to the LLM.
:::
#### Description
Description of this category.
You can input criteria, situation, or information that may help the LLM determine which inputs belong in this category.
#### Examples
Additional examples that may help the LLM determine which inputs belong in this category.
:::danger IMPORTANT
Examples are more helpful than the description if you want the LLM to classify particular cases into this category.
:::
#### Next step
Specifies the downstream component of this category.
- Once you specify the ID of the downstream component, a link is established between this category and the corresponding component.
- If you manually link this category to a downstream component on the canvas, the ID of that component is auto-populated.
## Examples
You can explore our customer service agent template, where a **Categorize** component (component ID: **Question Categorize**) has four defined categories and takes data inputs from an **Interact** component (component ID: **Interface**):
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Interpreter** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\concentrator.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 10
slug: /concentrator_component
---
# Concentrator component
A component that directs execution flow to multiple downstream components.
---
The **Concentrator** component acts as a "repeater" of execution flow, transmitting a flow to multiple downstream components.
## Scenarios
A **Concentrator** component enhances the current UX design. For a component originally designed to support only one downstream component, you can append a **Concentrator**, enabling it to have multiple downstream components.
## Examples
Explore our general-purpose chatbot agent template, featuring a **Concentrator** component (component ID: **medical**) that relays an execution flow from category 2 of the **Categorize** component to two translator components:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **General-purpose chatbot** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\generate.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 2
slug: /generate_component
---
# Generate component
The component that prompts the LLM to respond appropriately.
---
A **Generate** component fine-tunes the LLM and sets its prompt.
## Scenarios
A **Generate** component is essential when you need the LLM to assist with summarizing, translating, or controlling various tasks.
## Configurations
### Model
Click the dropdown menu of **Model** to show the model configuration window.
- **Model**: The chat model to use.
- Ensure you set the chat model correctly on the **Model providers** page.
- You can use different models for different components to increase flexibility or improve overall performance.
- **Freedom**: A shortcut to **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty** settings, indicating the freedom level of the model. From **Improvise**, **Precise**, to **Balance**, each preset configuration corresponds to a unique combination of **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**.
This parameter has three options:
- **Improvise**: Produces more creative responses.
- **Precise**: (Default) Produces more conservative responses.
- **Balance**: A middle ground between **Improvise** and **Precise**.
- **Temperature**: The randomness level of the model's output.
Defaults to 0.1.
- Lower values lead to more deterministic and predictable outputs.
- Higher values lead to more creative and varied outputs.
- A temperature of zero results in the same output for the same prompt.
- **Top P**: Nucleus sampling.
- Reduces the likelihood of generating repetitive or unnatural text by setting a threshold *P* and restricting the sampling to tokens with a cumulative probability exceeding *P*.
- Defaults to 0.3.
- **Presence penalty**: Encourages the model to include a more diverse range of tokens in the response.
- A higher **presence penalty** value results in the model being more likely to generate tokens not yet been included in the generated text.
- Defaults to 0.4.
- **Frequency penalty**: Discourages the model from repeating the same words or phrases too frequently in the generated text.
- A higher **frequency penalty** value results in the model being more conservative in its use of repeated tokens.
- Defaults to 0.7.
:::tip NOTE
- It is not necessary to stick with the same model for all components. If a specific model is not performing well for a particular task, consider using a different one.
- If you are uncertain about the mechanism behind **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**, simply choose one of the three options of **Preset configurations**.
:::
### System prompt
Typically, you use the system prompt to describe the task for the LLM, specify how it should respond, and outline other miscellaneous requirements. We do not plan to elaborate on this topic, as it can be as extensive as prompt engineering. However, please be aware that the system prompt is often used in conjunction with keys (variables), which serve as various data inputs for the LLM.
:::danger IMPORTANT
A **Generate** component relies on keys (variables) to specify its data inputs. Its immediate upstream component is *not* necessarily its data input, and the arrows in the workflow indicate *only* the processing sequence. Keys in a **Generate** component are used in conjunction with the system prompt to specify data inputs for the LLM. Use a forward slash `/` or the **(x)** button to show the keys to use.
:::
Below is a prompt excerpt of a **Generate** component from the **Interpreter** template (component ID: **Reflect**):
```text
Your task is to read a source text and a translation to {target_lang}, and give constructive suggestions to improve the translation. The source text and initial translation, delimited by XML tags <SOURCE_TEXT></SOURCE_TEXT> and <TRANSLATION></TRANSLATION>, are as follows:
<SOURCE_TEXT>
{source_text}
</SOURCE_TEXT>
<TRANSLATION>
{translation_1}
</TRANSLATION>
When writing suggestions, pay attention to whether there are ways to improve the translation's fluency, by applying {target_lang} grammar, spelling and punctuation rules, and ensuring there are no unnecessary repetitions.
- Each suggestion should address one specific part of the translation.
- Output the suggestions only.
```
Where `{source_text}` and `{target_lang}` are global variables defined by the **Begin** component, while `{translation_1}` is the output of another **Generate** component with the component ID **Translate directly**.
### Cite
This toggle sets whether to cite the original text as reference.
:::tip NOTE
This feature applies *only* after the original documents have been uploaded to the corresponding knowledge base(s) and file parsing is complete.
:::
### Message window size
An integer specifying the number of previous dialogue rounds to input into the LLM. For example, if it is set to 12, the tokens from the last 12 dialogue rounds will be fed to the LLM. This feature consumes additional tokens.
:::tip IMPORTANT
This feature is used for multi-turn dialogue *only*.
:::
## Examples
You can explore our three-step interpreter agent template, where a **Generate** component (component ID: **Reflect**) takes three global variables:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Interpreter** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on component **Reflect**, to display its **Configuration** window, where:
- `{target_lang}` and `{source_text}` are defined in the **Begin** component and require user input.
- `{translation_1}` is the output from the upstream component **Translate directly**.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\interact.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /interact_component
---
# Interact component
A component that accepts user inputs and displays responses.
---
An **Interact** component serves as the interface between human and bot, receiving user inputs and displaying the agent's responses.
## Scenarios
An **Interact** component is essential where you need to display the agent's responses or require user-computer interaction.
## Examples
You can explore our three-step interpreter agent template, where the **Interact** component is used to display the final translation, or our customer service agent template, where the **Interact** component is the immediate downstream of **Begin** and is used to display multi-turn dialogue between the user and the agent.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\iteration.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 12
slug: /iteration_component
---
# Iteration component
A component that splits text input into text segments and iterates a predefined workflow for each one.
---
An **Interaction** component can divide text input into text segments and apply its built-in component workflow to each segment.
## Scenario
An **Iteration** component is essential when a workflow loop is required and the loop count is *not* fixed but depends on number of segments created from the output of specific agent components.
- If, for instance, you plan to feed several paragraphs into an LLM for content generation, each with its own focus, and feeding them to the LLM all at once could create confusion or contradictions, then you can use an **Iteration** component, which encapsulates a **Generate** component, to repeat the content generation process for each paragraph.
- Another example: If you wish to use the LLM to translate a lengthy paper into a target language without exceeding its token limit, consider using an **Iteration** component, which encapsulates a **Generate** component, to break the paper into smaller pieces and repeat the translation process for each one.
## Internal components
### IterationItem
Each **Iteration** component includes an internal **IterationItem** component. The **IterationItem** component serves as both the starting point and input node of the workflow within the **Iteration** component. It manages the loop of the workflow for all text segments created from the input.
:::tip NOTE
The **IterationItem** component is visible *only* to the components encapsulated by the current **Iteration** components.
:::

### Build an internal workflow
You are allowed to pull other components into the **Iteration** component to build an internal workflow, and these "added internal components" are no longer visible to components outside of the current **Iteration** component.
:::danger IMPORTANT
To reference the created text segments from an added internal component, simply add a **Reference** variable that equals **IterationItem** within the **Input** section of that internal component. There is no need to reference the corresponding external component, as the **IterationItem** component manages the loop of the workflow for all created text segments.
:::
:::tip NOTE
An added internal component can reference an external component when necessary.
:::
## Configurations
### Input
The **Iteration** component uses input variables to specify its data inputs, namely the texts to be segmented. You are allowed to specify multiple input sources for the **Iteration** component. Click **+ Add variable** in the **Input** section to include the desired input variables. There are two types of input variables: **Reference** and **Text**.
- **Reference**: Uses a component's output or a user input as the data source. You are required to select from the dropdown menu:
- A component ID under **Component Output**, or
- A global variable under **Begin input**, which is defined in the **Begin** component.
- **Text**: Uses fixed text as the query. You are required to enter static text.
### Delimiter
The delimiter to use to split the text input into segments:
- Comma (Default)
- Line break
- Tab
- Underline
- Forward slash
- Dash
- Semicolon
## Examples
Explore our research report generator agent template, where the **Iteration** component (component ID: **Sections**) takes subtitles from the **Subtitles** component and generates sections for them:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Customer service** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Iteration** component to display its **Configuration** window.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\keyword.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 6
slug: /keyword_component
---
# Keyword component
A component that extracts keywords from a user query.
---
A **Keyword** component uses the specified LLM to extract keywords from a user query.
## Scenarios
A **Keyword** component is essential where you need to prepare keywords for a potential keyword search.
## Configurations
### Input
The **Keyword** component relies on input variables to specify its data inputs (queries). Click **+ Add variable** in the **Input** section to add the desired input variables. There are two types of input variables: **Reference** and **Text**.
- **Reference**: Uses a component's output or a user input as the data source. You are required to select from the dropdown menu:
- A component ID under **Component Output**, or
- A global variable under **Begin input**, which is defined in the **Begin** component.
- **Text**: Uses fixed text as the query. You are required to enter static text.
### Model
Click the dropdown menu of **Model** to show the model configuration window.
- **Model**: The chat model to use.
- Ensure you set the chat model correctly on the **Model providers** page.
- You can use different models for different components to increase flexibility or improve overall performance.
- **Freedom**: A shortcut to **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty** settings, indicating the freedom level of the model. From **Improvise**, **Precise**, to **Balance**, each preset configuration corresponds to a unique combination of **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**.
This parameter has three options:
- **Improvise**: Produces more creative responses.
- **Precise**: (Default) Produces more conservative responses.
- **Balance**: A middle ground between **Improvise** and **Precise**.
- **Temperature**: The randomness level of the model's output.
Defaults to 0.1.
- Lower values lead to more deterministic and predictable outputs.
- Higher values lead to more creative and varied outputs.
- A temperature of zero results in the same output for the same prompt.
- **Top P**: Nucleus sampling.
- Reduces the likelihood of generating repetitive or unnatural text by setting a threshold *P* and restricting the sampling to tokens with a cumulative probability exceeding *P*.
- Defaults to 0.3.
- **Presence penalty**: Encourages the model to include a more diverse range of tokens in the response.
- A higher **presence penalty** value results in the model being more likely to generate tokens not yet been included in the generated text.
- Defaults to 0.4.
- **Frequency penalty**: Discourages the model from repeating the same words or phrases too frequently in the generated text.
- A higher **frequency penalty** value results in the model being more conservative in its use of repeated tokens.
- Defaults to 0.7.
:::tip NOTE
- It is not necessary to stick with the same model for all components. If a specific model is not performing well for a particular task, consider using a different one.
- If you are uncertain about the mechanism behind **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**, simply choose one of the three options of **Preset**.
:::
### Number of keywords
An integer specifying the number of keywords to extract from the user query. Defaults to 3. Please note that the number of extracted keywords depends on the LLM's capabilities and the token count in the user query, and may *not* match the integer you set.
## Examples
Explore our general-purpose chatbot agent template, where the **Keyword** component (component ID: **keywords**) is used to extract keywords from financial inputs for a potential stock search in the **akshare** component:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **General-purpose chatbot** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Keyword** component to display its **Configuration** window.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\message.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 7
slug: /message_component
---
# Message component
A component that sends out a static message.
---
A **Message** component sends out a static message. If multiple messages are supplied, it randomly selects one to send.
## Configurations
### Messages
The message to send out.
Click **+ Add message** to add message options. When multiple messages are supplied, the **Message** component randomly selects one to send.
## Examples
Explore our customer service agent template, where the **Message** component (component ID: **What else?**) randomly sends out a message to the user interface if the user inputs is related to personal contact information:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Customer service** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Message** component to display its **Configuration** window.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\note.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 13
slug: /note_component
---
# Note component
The component that keeps design notes.
---
A **note** component allows you to keep design notes, including details about an agent, the output of specific components, the rationale of a particular design, or any information that may assist you, your users, or your fellow developers understand the agent.
## Examples
Explore our customer service agent template, which has five **Note** components:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Customer service** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **note** component to add or update notes.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\retrieval.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 4
slug: /retrieval_component
---
# Retrieval component
A component that retrieves information from specified datasets.
## Scenarios
A **Retrieval** component is essential in most RAG scenarios, where information is extracted from designated knowledge bases before being sent to the LLM for content generation.
## Configurations
Click on a **Retrieval** component to open its configuration window.
### Input
The **Retrieval** component relies on input variables to specify its data inputs (queries). Click **+ Add variable** in the **Input** section to add the desired input variables. There are two types of input variables: **Reference** and **Text**.
- **Reference**: Uses a component's output or a user input as the data source. You are required to select from the dropdown menu:
- A component ID under **Component Output**, or
- A global variable under **Begin input**, which is defined in the **Begin** component.
- **Text**: Uses fixed text as the query. You are required to enter static text.
### Similarity threshold
RAGFlow employs a combination of weighted keyword similarity and weighted vector cosine similarity during retrieval. This parameter sets the threshold for similarities between the user query and chunks stored in the datasets. Any chunk with a similarity score below this threshold will be excluded from the results.
Defaults to 0.2.
### Keyword similarity weight
This parameter sets the weight of keyword similarity in the combined similarity score. The total of the two weights must equal 1.0. Its default value is 0.7, which means the weight of vector similarity in the combined search is 1 - 0.7 = 0.3.
### Top N
This parameter selects the "Top N" chunks from retrieved ones and feed them to the LLM.
Defaults to 8.
### Rerank model
*Optional*
If a rerank model is selected, a combination of weighted keyword similarity and weighted reranking score will be used for retrieval.
:::caution WARNING
Using a rerank model will *significantly* increase the system's response time.
:::
### Tavily API key
*Optional*
Enter your Tavily API key here to enable Tavily web search during retrieval. See [here](https://app.tavily.com/home) for instructions on getting a Tavily API key.
### Use knowledge graph
Whether to use knowledge graph(s) in the specified knowledge base(s) during retrieval for multi-hop question answering. When enabled, this would involve iterative searches across entity, relationship, and community report chunks, greatly increasing retrieval time.
### Knowledge bases
*Optional*
Select the knowledge base(s) to retrieve data from.
- If no knowledge base is selected, meaning conversations with the agent will not be based on any knowledge base, ensure that the **Empty response** field is left blank to avoid an error.
- If you select multiple knowledge bases, you must ensure that the knowledge bases (datasets) you select use the same embedding model; otherwise, an error message would occur.
### Empty response
- Set this as a response if no results are retrieved from the knowledge base(s) for your query, or
- Leave this field blank to allow the chat model to improvise when nothing is found.
:::caution WARNING
If you do not specify a knowledge base, you must leave this field blank; otherwise, an error would occur.
:::
## Examples
Explore our customer service agent template, where the **Retrieval** component (component ID: **Search product info**) is used to search the dataset and send the Top N results to the LLM:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Customer service** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Retrieval** component to display its **Configuration** window.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\rewrite.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 8
slug: /rewrite_component
---
# Rewrite component
A component that rewrites a user query.
---
A **Rewrite** component uses a specified LLM to rewrite a user query from the **Interact** component, based on the context of previous dialogues.
## Scenarios
A **Rewrite** component is essential when you need to optimize a user query based on the context of previous conversations. It is usually the upstream component of a **Retrieval** component.
:::tip NOTE
See also the [Keyword](./keyword.mdx) component, a similar component used for multi-turn optimization.
:::
## Configurations
:::tip NOTE
The **Rewrite** component uses the user-agent interaction from the **Interact** component as its data input. Therefore, there is no need to specify its data inputs in the Configurations.
:::
### Model
Click the dropdown menu of **Model** to show the model configuration window.
- **Model**: The chat model to use.
- Ensure you set the chat model correctly on the **Model providers** page.
- You can use different models for different components to increase flexibility or improve overall performance.
- **Freedom**: A shortcut to **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty** settings, indicating the freedom level of the model. From **Improvise**, **Precise**, to **Balance**, each preset configuration corresponds to a unique combination of **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**.
This parameter has three options:
- **Improvise**: Produces more creative responses.
- **Precise**: (Default) Produces more conservative responses.
- **Balance**: A middle ground between **Improvise** and **Precise**.
- **Temperature**: The randomness level of the model's output.
Defaults to 0.1.
- Lower values lead to more deterministic and predictable outputs.
- Higher values lead to more creative and varied outputs.
- A temperature of zero results in the same output for the same prompt.
- **Top P**: Nucleus sampling.
- Reduces the likelihood of generating repetitive or unnatural text by setting a threshold *P* and restricting the sampling to tokens with a cumulative probability exceeding *P*.
- Defaults to 0.3.
- **Presence penalty**: Encourages the model to include a more diverse range of tokens in the response.
- A higher **presence penalty** value results in the model being more likely to generate tokens not yet been included in the generated text.
- Defaults to 0.4.
- **Frequency penalty**: Discourages the model from repeating the same words or phrases too frequently in the generated text.
- A higher **frequency penalty** value results in the model being more conservative in its use of repeated tokens.
- Defaults to 0.7.
:::tip NOTE
- It is not necessary to stick with the same model for all components. If a specific model is not performing well for a particular task, consider using a different one.
- If you are uncertain about the mechanism behind **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**, simply choose one of the three options of **Preset configurations**.
:::
### Message window size
An integer specifying the number of previous dialogue rounds to input into the LLM. For example, if it is set to 12, the tokens from the last 12 dialogue rounds will be fed to the LLM. This feature consumes additional tokens.
Defaults to 1.
:::tip IMPORTANT
This feature is used for multi-turn dialogue *only*. If your **Categorize** component is not part of a multi-turn dialogue (i.e., it is not in a loop), leave this field as-is.
:::
## Examples
Explore our customer service agent template, where the **Rewrite** component (component ID: **Refine Question**) is used to optimize a product-specific user query based on context of previous dialogues before passing it on to the **Retrieval** component.
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Customer service** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Rewrite** component to display its **Configuration** window.
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\switch.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 9
slug: /switch_component
---
# Switch component
A component that evaluates whether specified conditions are met and directs the follow of execution accordingly.
---
A **Switch** component evaluates conditions based on the output of specific components, directing the flow of execution accordingly to enable complex branching logic.
## Scenarios
A **Switch** component is essential for condition-based direction of execution flow. While it shares similarities with the [Categorize](./categorize.mdx) component, which is also used in multi-pronged strategies, the key distinction lies in their approach: the evaluation of the **Switch** component is rule-based, whereas the **Categorize** component involves AI and uses an LLM for decision-making.
## Configurations
### Case n
A **Switch** component must have at least one case, each with multiple specified conditions and *only one* downstream component. When multiple conditions are specified for a case, you must set the logical relationship between them to either AND or OR.
#### Next step
Specifies the downstream component of this case.
- *Once you specify the ID of the downstream component, a link is established between this case and the corresponding component.*
- *If you manually link this case to a downstream component on the canvas, the ID of that component is auto-populated.*
#### Condition
Evaluates whether the output of specific components meets certain conditions, with **Component ID**, **Operator**, and **Value** together forming a conditional expression.
:::danger IMPORTANT
When you have added multiple conditions for a specific case, a **Logical operator** field appears, requiring you to set the logical relationship between these conditions as either AND or OR.

:::
- **Component ID**: The ID of the corresponding component.
- **Operator**: The operator required to form a conditional expression.
- Equals
- Not equal
- Greater than
- Greater equal
- Less than
- Less equal
- Contains
- Not contains
- Starts with
- Ends with
- Is empty
- Not empty
- **Value**: A single value, which can be an integer, float, or string.
- Delimiters, multiple values, or expressions are *not* supported.
- Strings need not be wrapped in `""` or `''`.
### ELSE
**Required**. Specifies the downstream component if none of the conditions defined above are met.
*Once you specify the ID of the downstream component, a link is established between ELSE and the corresponding component.*
guides\agent\agent_component_reference\template.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 11
slug: /template_component
---
# Template component
A component that formats user inputs or the outputs of other components.
---
A **Template** component acts as a content formatter. It is usually the upstream component of an **Interact** component.
## Scenarios
A **Template** component is useful for organizing various sources of data or information into specific formats.
## Configurations
### Content
Used together with Keys to organize various data or information sources into desired formats. Example:
```text
<h2>{subtitle}</h2>
<div>{content}</div>
```
Where `{subtitle}` and `{content}` are defined keys.
### Key
A **Template** component relies on keys (variables) to specify its data or information sources. Its immediate upstream component is *not* necessarily its input, and the arrows in the workflow indicate *only* the processing sequence.
Values of keys are categorized into two groups:
- **Component Output**: The value of the key should be a component ID.
- **Begin Input**: The value of the key should be the name of a global variable defined in the **Begin** component.
## Examples
Explore our research report generator agent template, where the **Template** component (component ID: **Article**) organizes user input and the outputs of the **Sections** component into HTML format:
1. Click the **Agent** tab at the top center of the page to access the **Agent** page.
2. Click **+ Create agent** on the top right of the page to open the **agent template** page.
3. On the **agent template** page, hover over the **Research report generator** card and click **Use this template**.
4. Name your new agent and click **OK** to enter the workflow editor.
5. Click on the **Template** component to display its **Configuration** window
guides\chat_category_.json
{
"label": "Chat",
"position": 1,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Chat-specific guides."
}
}
guides\chat\implement_deep_research.md
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /implement_deep_research
---
# Implement deep research
Implements deep research for agentic reasoning.
---
From v0.17.0 onward, RAGFlow supports integrating agentic reasoning in an AI chat. The following diagram illustrates the workflow of RAGFlow's deep research:

To activate this feature:
1. Enable the **Reasoning** toggle under the **Prompt engine** tab of your chat assistant dialogue.

2. Enter the correct Tavily API key under the **Assistant settings** tab of your chat assistant dialogue to leverage Tavily-based web search

*The following is a screenshot of a conversation that integrates Deep Research:*

guides\chat\set_chat_variables.md
---
sidebar_position: 4
slug: /set_chat_variables
---
# Set variables
Set variables to be used together with the system prompt for your LLM.
---
When configuring the system prompt for a chat model, variables play an important role in enhancing flexibility and reusability. With variables, you can dynamically adjust the system prompt to be sent to your model. In the context of RAGFlow, if you have defined variables in the **Chat Configuration** dialogue, except for the system's reserved variable `{knowledge}`, you are required to pass in values for them from RAGFlow's [HTTP API](../../references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant) or through its [Python SDK](../../references/python_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant).
:::danger IMPORTANT
In RAGFlow, variables are closely linked with the system prompt. When you add a variable in the **Variable** section, include it in the system prompt. Conversely, when deleting a variable, ensure it is removed from the system prompt; otherwise, an error would occur.
:::
## Where to set variables
Hover your mouse over your chat assistant, click **Edit** to open its **Chat Configuration** dialogue, then click the **Prompt engine** tab. Here, you can work on your variables in the **System prompt** field and the **Variable** section:
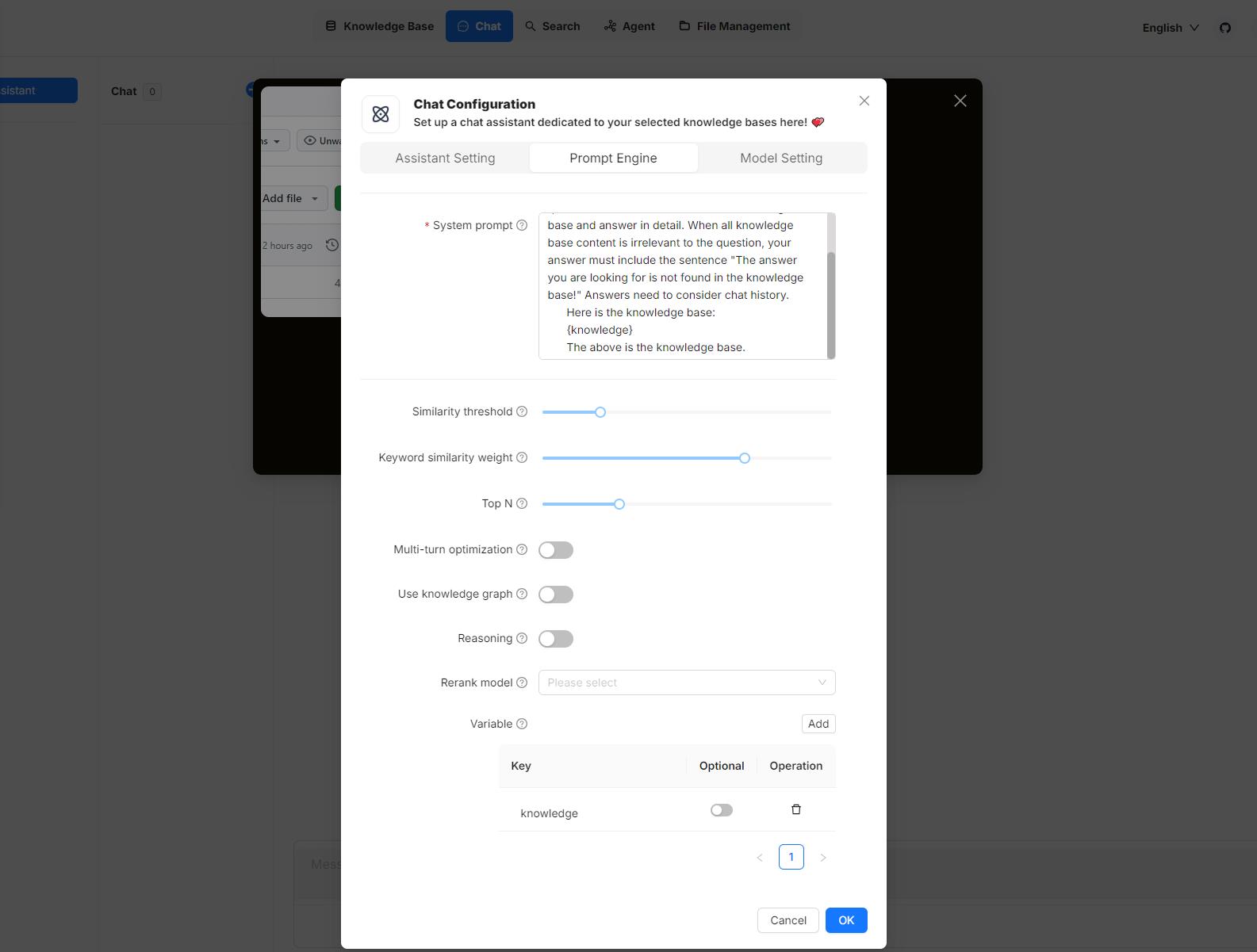
## 1. Manage variables
In the **Variable** section, you add, remove, or update variables.
### `{knowledge}` - a reserved variable
`{knowledge}` is the system's reserved variable, representing the chunks retrieved from the knowledge base(s) specified by **Knowledge bases** under the **Assistant settings** tab. If your chat assistant is associated with certain knowledge bases, you can keep it as is.
:::info NOTE
It does not currently make a difference whether you set `{knowledge}` to optional or mandatory, but note that this design will be updated at a later point.
:::
From v0.17.0 onward, you can start an AI chat without specifying knowledge bases. In this case, we recommend removing the `{knowledge}` variable to prevent unnecessary reference and keeping the **Empty response** field empty to avoid errors.
### Custom variables
Besides `{knowledge}`, you can also define your own variables to pair with the system prompt. To use these custom variables, you must pass in their values through RAGFlow's official APIs. The **Optional** toggle determines whether these variables are required in the corresponding APIs:
- **Disabled** (Default): The variable is mandatory and must be provided.
- **Enabled**: The variable is optional and can be omitted if not needed.
## 2. Update system prompt
After you add or remove variables in the **Variable** section, ensure your changes are reflected in the system prompt to avoid inconsistencies or errors. Here's an example:
```
You are an intelligent assistant. Please answer the question by summarizing chunks from the specified knowledge base(s)...
Your answers should follow a professional and {style} style.
...
Here is the knowledge base:
{knowledge}
The above is the knowledge base.
```
:::tip NOTE
If you have removed `{knowledge}`, ensure that you thoroughly review and update the entire system prompt to achieve optimal results.
:::
## APIs
The *only* way to pass in values for the custom variables defined in the **Chat Configuration** dialogue is to call RAGFlow's [HTTP API](../../references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant) or through its [Python SDK](../../references/python_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant).
### HTTP API
See [Converse with chat assistant](../../references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant). Here's an example:
```json {9}
curl --request POST \
--url http://{address}/api/v1/chats/{chat_id}/completions \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_API_KEY>' \
--data-binary '
{
"question": "xxxxxxxxx",
"stream": true,
"style":"hilarious"
}'
```
### Python API
See [Converse with chat assistant](../../references/python_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant). Here's an example:
```python {18}
from ragflow_sdk import RAGFlow
rag_object = RAGFlow(api_key="<YOUR_API_KEY>", base_url="http://<YOUR_BASE_URL>:9380")
assistant = rag_object.list_chats(name="Miss R")
assistant = assistant[0]
session = assistant.create_session()
print("\n==================== Miss R =====================\n")
print("Hello. What can I do for you?")
while True:
question = input("\n==================== User =====================\n> ")
style = input("Please enter your preferred style (e.g., formal, informal, hilarious): ")
print("\n==================== Miss R =====================\n")
cont = ""
for ans in session.ask(question, stream=True, style=style):
print(ans.content[len(cont):], end='', flush=True)
cont = ans.content
```
guides\chat\start_chat.md
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /start_chat
---
# Start AI chat
Initiate an AI-powered chat with a configured chat assistant.
---
Knowledge base, hallucination-free chat, and file management are the three pillars of RAGFlow. Chats in RAGFlow are based on a particular knowledge base or multiple knowledge bases. Once you have created your knowledge base, finished file parsing, and [run a retrieval test](../dataset/run_retrieval_test.md), you can go ahead and start an AI conversation.
## Start an AI chat
You start an AI conversation by creating an assistant.
1. Click the **Chat** tab in the middle top of the page **>** **Create an assistant** to show the **Chat Configuration** dialogue *of your next dialogue*.
> RAGFlow offers you the flexibility of choosing a different chat model for each dialogue, while allowing you to set the default models in **System Model Settings**.
2. Update **Assistant settings**:
- **Assistant name** is the name of your chat assistant. Each assistant corresponds to a dialogue with a unique combination of knowledge bases, prompts, hybrid search configurations, and large model settings.
- **Empty response**:
- If you wish to *confine* RAGFlow's answers to your knowledge bases, leave a response here. Then, when it doesn't retrieve an answer, it *uniformly* responds with what you set here.
- If you wish RAGFlow to *improvise* when it doesn't retrieve an answer from your knowledge bases, leave it blank, which may give rise to hallucinations.
- **Show quote**: This is a key feature of RAGFlow and enabled by default. RAGFlow does not work like a black box. Instead, it clearly shows the sources of information that its responses are based on.
- Select the corresponding knowledge bases. You can select one or multiple knowledge bases, but ensure that they use the same embedding model, otherwise an error would occur.
3. Update **Prompt engine**:
- In **System**, you fill in the prompts for your LLM, you can also leave the default prompt as-is for the beginning.
- **Similarity threshold** sets the similarity "bar" for each chunk of text. The default is 0.2. Text chunks with lower similarity scores are filtered out of the final response.
- **Keyword similarity weight** is set to 0.7 by default. RAGFlow uses a hybrid score system to evaluate the relevance of different text chunks. This value sets the weight assigned to the keyword similarity component in the hybrid score.
- If **Rerank model** is left empty, the hybrid score system uses keyword similarity and vector similarity, and the default weight assigned to the vector similarity component is 1-0.7=0.3.
- If **Rerank model** is selected, the hybrid score system uses keyword similarity and reranker score, and the default weight assigned to the reranker score is 1-0.7=0.3.
- **Top N** determines the *maximum* number of chunks to feed to the LLM. In other words, even if more chunks are retrieved, only the top N chunks are provided as input.
- **Multi-turn optimization** enhances user queries using existing context in a multi-round conversation. It is enabled by default. When enabled, it will consume additional LLM tokens and significantly increase the time to generate answers.
- **Use knowledge graph** indicates whether to use knowledge graph(s) in the specified knowledge base(s) during retrieval for multi-hop question answering. When enabled, this would involve iterative searches across entity, relationship, and community report chunks, greatly increasing retrieval time.
- **Reasoning** indicates whether to generate answers through reasoning processes like Deepseek-R1/OpenAI o1. Once enabled, the chat model autonomously integrates Deep Research during question answering when encountering an unknown topic. This involves the chat model dynamically searching external knowledge and generating final answers through reasoning.
- **Rerank model** sets the reranker model to use. It is left empty by default.
- If **Rerank model** is left empty, the hybrid score system uses keyword similarity and vector similarity, and the default weight assigned to the vector similarity component is 1-0.7=0.3.
- If **Rerank model** is selected, the hybrid score system uses keyword similarity and reranker score, and the default weight assigned to the reranker score is 1-0.7=0.3.
- **Variable** refers to the variables (keys) to be used in the system prompt. `{knowledge}` is a reserved variable. Click **Add** to add more variables for the system prompt.
- If you are uncertain about the logic behind **Variable**, leave it *as-is*.
- As of v0.18.0, if you add custom variables here, the only way you can pass in their values is to call:
- HTTP method [Converse with chat assistant](../../references/http_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant), or
- Python method [Converse with chat assistant](../../references/python_api_reference.md#converse-with-chat-assistant).
4. Update **Model Setting**:
- In **Model**: you select the chat model. Though you have selected the default chat model in **System Model Settings**, RAGFlow allows you to choose an alternative chat model for your dialogue.
- **Freedom**: A shortcut to **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty** settings, indicating the freedom level of the model. From **Improvise**, **Precise**, to **Balance**, each preset configuration corresponds to a unique combination of **Temperature**, **Top P**, **Presence penalty**, and **Frequency penalty**.
This parameter has three options:
- **Improvise**: Produces more creative responses.
- **Precise**: (Default) Produces more conservative responses.
- **Balance**: A middle ground between **Improvise** and **Precise**.
- **Temperature**: The randomness level of the model's output.
Defaults to 0.1.
- Lower values lead to more deterministic and predictable outputs.
- Higher values lead to more creative and varied outputs.
- A temperature of zero results in the same output for the same prompt.
- **Top P**: Nucleus sampling.
- Reduces the likelihood of generating repetitive or unnatural text by setting a threshold *P* and restricting the sampling to tokens with a cumulative probability exceeding *P*.
- Defaults to 0.3.
- **Presence penalty**: Encourages the model to include a more diverse range of tokens in the response.
- A higher **presence penalty** value results in the model being more likely to generate tokens not yet been included in the generated text.
- Defaults to 0.4.
- **Frequency penalty**: Discourages the model from repeating the same words or phrases too frequently in the generated text.
- A higher **frequency penalty** value results in the model being more conservative in its use of repeated tokens.
- Defaults to 0.7.
5. Now, let's start the show:

:::tip NOTE
1. Click the light bulb icon above the answer to view the expanded system prompt:

*The light bulb icon is available only for the current dialogue.*
2. Scroll down the expanded prompt to view the time consumed for each task:

:::
## Update settings of an existing chat assistant
Hover over an intended chat assistant **>** **Edit** to show the chat configuration dialogue:


## Integrate chat capabilities into your application or webpage
RAGFlow offers HTTP and Python APIs for you to integrate RAGFlow's capabilities into your applications. Read the following documents for more information:
- [Acquire a RAGFlow API key](../../develop/acquire_ragflow_api_key.md)
- [HTTP API reference](../../references/http_api_reference.md)
- [Python API reference](../../references/python_api_reference.md)
You can use iframe to embed the created chat assistant into a third-party webpage:
1. Before proceeding, you must [acquire an API key](../models/llm_api_key_setup.md); otherwise, an error message would appear.
2. Hover over an intended chat assistant **>** **Edit** to show the **iframe** window:

3. Copy the iframe and embed it into a specific location on your webpage.
guides\chat\best_practices_category_.json
{
"label": "Best practices",
"position": 7,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Best practices on chat assistant configuration."
}
}
guides\chat\best_practices\accelerate_question_answering.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /accelerate_question_answering
---
# Accelerate answering
import APITable from '@site/src/components/APITable';
A checklist to speed up question answering.
---
Please note that some of your settings may consume a significant amount of time. If you often find that your question answering is time-consuming, here is a checklist to consider:
- In the **Prompt engine** tab of your **Chat Configuration** dialogue, disabling **Multi-turn optimization** will reduce the time required to get an answer from the LLM.
- In the **Prompt engine** tab of your **Chat Configuration** dialogue, leaving the **Rerank model** field empty will significantly decrease retrieval time.
- When using a rerank model, ensure you have a GPU for acceleration; otherwise, the reranking process will be *prohibitively* slow.
:::tip NOTE
Please note that rerank models are essential in certain scenarios. There is always a trade-off between speed and performance; you must weigh the pros against cons for your specific case.
:::
- In the **Assistant settings** tab of your **Chat Configuration** dialogue, disabling **Keyword analysis** will reduce the time to receive an answer from the LLM.
- When chatting with your chat assistant, click the light bulb icon above the *current* dialogue and scroll down the popup window to view the time taken for each task:

```mdx-code-block
<APITable>
```
| Item name | Description |
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Total | Total time spent on this conversation round, including chunk retrieval and answer generation. |
| Check LLM | Time to validate the specified LLM. |
| Create retriever | Time to create a chunk retriever. |
| Bind embedding | Time to initialize an embedding model instance. |
| Bind LLM | Time to initialize an LLM instance. |
| Tune question | Time to optimize the user query using the context of the mult-turn conversation. |
| Bind reranker | Time to initialize an reranker model instance for chunk retrieval. |
| Generate keywords | Time to extract keywords from the user query. |
| Retrieval | Time to retrieve the chunks. |
| Generate answer | Time to generate the answer. |
```mdx-code-block
</APITable>
```
guides\dataset_category_.json
{
"label": "Datasets",
"position": 0,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Guides on configuring a knowledge base."
}
}
guides\dataset\configure_knowledge_base.md
---
sidebar_position: 0
slug: /configure_knowledge_base
---
# Configure knowledge base
Knowledge base, hallucination-free chat, and file management are the three pillars of RAGFlow. RAGFlow's AI chats are based on knowledge bases. Each of RAGFlow's knowledge bases serves as a knowledge source, *parsing* files uploaded from your local machine and file references generated in **File Management** into the real 'knowledge' for future AI chats. This guide demonstrates some basic usages of the knowledge base feature, covering the following topics:
- Create a knowledge base
- Configure a knowledge base
- Search for a knowledge base
- Delete a knowledge base
## Create knowledge base
With multiple knowledge bases, you can build more flexible, diversified question answering. To create your first knowledge base:

_Each time a knowledge base is created, a folder with the same name is generated in the **root/.knowledgebase** directory._
## Configure knowledge base
The following screenshot shows the configuration page of a knowledge base. A proper configuration of your knowledge base is crucial for future AI chats. For example, choosing the wrong embedding model or chunking method would cause unexpected semantic loss or mismatched answers in chats.

This section covers the following topics:
- Select chunking method
- Select embedding model
- Upload file
- Parse file
- Intervene with file parsing results
- Run retrieval testing
### Select chunking method
RAGFlow offers multiple chunking template to facilitate chunking files of different layouts and ensure semantic integrity. In **Chunking method**, you can choose the default template that suits the layouts and formats of your files. The following table shows the descriptions and the compatible file formats of each supported chunk template:
| **Template** | Description | File format |
|--------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| General | Files are consecutively chunked based on a preset chunk token number. | DOCX, XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), PPT, PDF, TXT, JPEG, JPG, PNG, TIF, GIF, CSV, JSON, EML, HTML |
| Q&A | | XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), CSV/TXT |
| Resume | Enterprise edition only. You can also try it out on demo.ragflow.io. | DOCX, PDF, TXT |
| Manual | | PDF |
| Table | | XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), CSV/TXT |
| Paper | | PDF |
| Book | | DOCX, PDF, TXT |
| Laws | | DOCX, PDF, TXT |
| Presentation | | PDF, PPTX |
| Picture | | JPEG, JPG, PNG, TIF, GIF |
| One | Each document is chunked in its entirety (as one). | DOCX, XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), PDF, TXT |
| Tag | The knowledge base functions as a tag set for the others. | XLSX, CSV/TXT |
You can also change a file's chunking method on the **Datasets** page.

### Select embedding model
An embedding model converts chunks into embeddings. It cannot be changed once the knowledge base has chunks. To switch to a different embedding model, you must delete all existing chunks in the knowledge base. The obvious reason is that we *must* ensure that files in a specific knowledge base are converted to embeddings using the *same* embedding model (ensure that they are compared in the same embedding space).
The following embedding models can be deployed locally:
- BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5
- maidalun1020/bce-embedding-base_v1
### Upload file
- RAGFlow's **File Management** allows you to link a file to multiple knowledge bases, in which case each target knowledge base holds a reference to the file.
- In **Knowledge Base**, you are also given the option of uploading a single file or a folder of files (bulk upload) from your local machine to a knowledge base, in which case the knowledge base holds file copies.
While uploading files directly to a knowledge base seems more convenient, we *highly* recommend uploading files to **File Management** and then linking them to the target knowledge bases. This way, you can avoid permanently deleting files uploaded to the knowledge base.
### Parse file
File parsing is a crucial topic in knowledge base configuration. The meaning of file parsing in RAGFlow is twofold: chunking files based on file layout and building embedding and full-text (keyword) indexes on these chunks. After having selected the chunking method and embedding model, you can start parsing a file:

- Click the play button next to **UNSTART** to start file parsing.
- Click the red-cross icon and then refresh, if your file parsing stalls for a long time.
- As shown above, RAGFlow allows you to use a different chunking method for a particular file, offering flexibility beyond the default method.
- As shown above, RAGFlow allows you to enable or disable individual files, offering finer control over knowledge base-based AI chats.
### Intervene with file parsing results
RAGFlow features visibility and explainability, allowing you to view the chunking results and intervene where necessary. To do so:
1. Click on the file that completes file parsing to view the chunking results:
_You are taken to the **Chunk** page:_

2. Hover over each snapshot for a quick view of each chunk.
3. Double-click the chunked texts to add keywords or make *manual* changes where necessary:

:::caution NOTE
You can add keywords to a file chunk to increase its ranking for queries containing those keywords. This action increases its keyword weight and can improve its position in search list.
:::
4. In Retrieval testing, ask a quick question in **Test text** to double-check if your configurations work:
_As you can tell from the following, RAGFlow responds with truthful citations._

### Run retrieval testing
RAGFlow uses multiple recall of both full-text search and vector search in its chats. Prior to setting up an AI chat, consider adjusting the following parameters to ensure that the intended information always turns up in answers:
- Similarity threshold: Chunks with similarities below the threshold will be filtered. By default, it is set to 0.2.
- Vector similarity weight: The percentage by which vector similarity contributes to the overall score. By default, it is set to 0.3.
See [Run retrieval test](./run_retrieval_test.md) for details.

## Search for knowledge base
As of RAGFlow v0.18.0, the search feature is still in a rudimentary form, supporting only knowledge base search by name.

## Delete knowledge base
You are allowed to delete a knowledge base. Hover your mouse over the three dot of the intended knowledge base card and the **Delete** option appears. Once you delete a knowledge base, the associated folder under **root/.knowledge** directory is AUTOMATICALLY REMOVED. The consequence is:
- The files uploaded directly to the knowledge base are gone;
- The file references, which you created from within **File Management**, are gone, but the associated files still exist in **File Management**.

guides\dataset\construct_knowledge_graph.md
---
sidebar_position: 8
slug: /construct_knowledge_graph
---
# Construct knowledge graph
Generate a knowledge graph for your knowledge base.
---
To enhance multi-hop question-answering, RAGFlow adds a knowledge graph construction step between data extraction and indexing, as illustrated below. This step creates additional chunks from existing ones generated by your specified chunking method.

From v0.16.0 onward, RAGFlow supports constructing a knowledge graph on a knowledge base, allowing you to construct a *unified* graph across multiple files within your knowledge base. When a newly uploaded file starts parsing, the generated graph will automatically update.
:::danger WARNING
Constructing a knowledge graph requires significant memory, computational resources, and tokens.
:::
## Scenarios
Knowledge graphs are especially useful for multi-hop question-answering involving *nested* logic. They outperform traditional extraction approaches when you are performing question answering on books or works with complex entities and relationships.
:::tip NOTE
RAPTOR (Recursive Abstractive Processing for Tree Organized Retrieval) can also be used for multi-hop question-answering tasks. See [Enable RAPTOR](./enable_raptor.md) for details. You may use either approach or both, but ensure you understand the memory, computational, and token costs involved.
:::
## Prerequisites
The system's default chat model is used to generate knowledge graph. Before proceeding, ensure that you have a chat model properly configured:

## Configurations
### Entity types (*Required*)
The types of the entities to extract from your knowledge base. The default types are: **organization**, **person**, **event**, and **category**. Add or remove types to suit your specific knowledge base.
### Method
The method to use to construct knowledge graph:
- **General**: Use prompts provided by [GraphRAG](https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag) to extract entities and relationships.
- **Light**: (Default) Use prompts provided by [LightRAG](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG) to extract entities and relationships. This option consumes fewer tokens, less memory, and fewer computational resources.
### Entity resolution
Whether to enable entity resolution. You can think of this as an entity deduplication switch. When enabled, the LLM will combine similar entities - e.g., '2025' and 'the year of 2025', or 'IT' and 'Information Technology' - to construct a more effective graph.
- (Default) Disable entity resolution.
- Enable entity resolution. This option consumes more tokens.
### Community report generation
In a knowledge graph, a community is a cluster of entities linked by relationships. You can have the LLM generate an abstract for each community, known as a community report. See [here](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-improving-global-search-via-dynamic-community-selection/) for more information. This indicates whether to generate community reports:
- Generate community reports. This option consumes more tokens.
- (Default) Do not generate community reports.
## Procedure
1. On the **Configuration** page of your knowledge base, switch on **Extract knowledge graph** or adjust its settings as needed, and click **Save** to confirm your changes.
- *The default knowledge graph configurations for your knowledge base are now set and files uploaded from this point onward will automatically use these settings during parsing.*
- *Files parsed before this update will retain their original knowledge graph settings.*
2. The knowledge graph of your knowledge base does *not* automatically update *until* a newly uploaded file is parsed.
_A **Knowledge graph** entry appears under **Configuration** once a knowledge graph is created._
3. Click **Knowledge graph** to view the details of the generated graph.
4. To use the created knowledge graph, do either of the following:
- In your **Chat Configuration** dialogue, click the **Assistant settings** tab to add the corresponding knowledge base(s) and click the **Prompt engine** tab to switch on the **Use knowledge graph** toggle.
- If you are using an agent, click the **Retrieval** agent component to specify the knowledge base(s) and switch on the **Use knowledge graph** toggle.
## Frequently asked questions
### Can I have different knowledge graph settings for different files in my knowledge base?
Yes, you can. Just one graph is generated per knowledge base. The smaller graphs of your files will be *combined* into one big, unified graph at the end of the graph extraction process.
### Does the knowledge graph automatically update when I remove a related file?
Nope. The knowledge graph does *not* automatically update *until* a newly uploaded document is parsed.
### How to remove a generated knowledge graph?
To remove the generated knowledge graph, delete all related files in your knowledge base. Although the **Knowledge graph** entry will still be visible, the graph has actually been deleted.
### Where is the created knowledge graph stored?
All chunks of the created knowledge graph are stored in RAGFlow's document engine: either Elasticsearch or [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity).
guides\dataset\enable_excel2html.md
---
sidebar_position: 4
slug: /enable_excel2html
---
# Enable Excel2HTML
Convert complex Excel spreadsheets into HTML tables.
---
When using the General chunking method, you can enable the **Excel to HTML** toggle to convert spreadsheet files into HTML tables. If it is disabled, spreadsheet tables will be represented as key-value pairs. For complex tables that cannot be simply represented this way, you must enable this feature.
:::caution WARNING
The feature is disabled by default. If your knowledge base contains spreadsheets with complex tables and you do not enable this feature, RAGFlow will not throw an error but your tables are likely to be garbled.
:::
## Scenarios
Works with complex tables that cannot be represented as key-value pairs. Examples include spreadsheet tables with multiple columns, tables with merged cells, or multiple tables within one sheet. In such cases, consider converting these spreadsheet tables into HTML tables.
## Considerations
- The Excel2HTML feature applies only to spreadsheet files (XLSX or XLS (Excel 97-2003)).
- This feature is associated with the General chunking method. In other words, it is available *only when* you select the General chunking method.
- When this feature is enabled, spreadsheet tables with more than 12 rows will be split into chunks of 12 rows each.
## Procedure
1. On your knowledge base's **Configuration** page, select **General** as the chunking method.
_The **Excel to HTML** toggle appears._
2. Enable **Excel to HTML** if your knowledge base contains complex spreadsheet tables that cannot be represented as key-value pairs.
3. Leave **Excel to HTML** disabled if your knowledge base has no spreadsheet tables or if its spreadsheet tables can be represented as key-value pairs.
4. If question-answering regarding complex tables is unsatisfactory, check if **Excel to HTML** is enabled.
## Frequently asked questions
### Should I enable this feature for PDFs with complex tables?
Nope. This feature applies to spreadsheet files only. Enabling **Excel to HTML** does not affect your PDFs.
guides\dataset\enable_raptor.md
---
sidebar_position: 7
slug: /enable_raptor
---
# Enable RAPTOR
A recursive abstractive method used in long-context knowledge retrieval and summarization, balancing broad semantic understanding with fine details.
---
RAPTOR (Recursive Abstractive Processing for Tree Organized Retrieval) is an enhanced document preprocessing technique introduced in a [2024 paper](https://arxiv.org/html/2401.18059v1). Designed to tackle multi-hop question-answering issues, RAPTOR performs recursive clustering and summarization of document chunks to build a hierarchical tree structure. This enables more context-aware retrieval across lengthy documents. RAGFlow v0.6.0 integrates RAPTOR for document clustering as part of its data preprocessing pipeline between data extraction and indexing, as illustrated below.
Our tests with this new approach demonstrate state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on question-answering tasks requiring complex, multi-step reasoning. By combining RAPTOR retrieval with our built-in chunking methods and/or other retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approaches, you can further improve your question-answering accuracy.
:::danger WARNING
Enabling RAPTOR requires significant memory, computational resources, and tokens.
:::
## Basic principles
After the original documents are divided into chunks, the chunks are clustered by semantic similarity rather than by their original order in the text. Clusters are then summarized into higher-level chunks by your system's default chat model. This process is applied recursively, forming a tree structure with various levels of summarization from the bottom up. As illustrated in the figure below, the initial chunks form the leaf nodes (shown in blue) and are recursively summarized into a root node (shown in orange).
The recursive clustering and summarization capture a broad understanding (by the root node) as well as fine details (by the leaf nodes) necessary for multi-hop question-answering.
## Scenarios
For multi-hop question-answering tasks involving complex, multi-step reasoning, a semantic gap often exists between the question and its answer. As a result, searching with the question often fails to retrieve the relevant chunks that contribute to the correct answer. RAPTOR addresses this challenge by providing the chat model with richer and more context-aware and relevant chunks to summarize, enabling a holistic understanding without losing granular details.
:::tip NOTE
Knowledge graphs can also be used for multi-hop question-answering tasks. See [Construct knowledge graph](./construct_knowledge_graph.md) for details. You may use either approach or both, but ensure you understand the memory, computational, and token costs involved.
:::
## Prerequisites
The system's default chat model is used to summarize clustered content. Before proceeding, ensure that you have a chat model properly configured:

## Configurations
The RAPTOR feature is disabled by default. To enable it, manually switch on the **Use RAPTOR to enhance retrieval** toggle on your knowledge base's **Configuration** page.
### Prompt
The following prompt will be applied recursively for cluster summarization, with `{cluster_content}` serving as an internal parameter. We recommend that you keep it as-is for now. The design will be updated at a later point.
```
Please summarize the following paragraphs... Paragraphs as following:
{cluster_content}
The above is the content you need to summarize.
```
### Max token
The maximum number of tokens per generated summary chunk. Defaults to 256, with a maximum limit of 2048.
### Threshold
In RAPTOR, chunks are clustered by their semantic similarity. The **Threshold** parameter sets the minimum similarity required for chunks to be grouped together.
It defaults to 0.1, with a maximum limit of 1. A higher **Threshold** means fewer chunks in each cluster, while a lower one means more.
### Max cluster
The maximum number of clusters to create. Defaults to 64, with a maximum limit of 1024.
### Random seed
A random seed. Click **+** to change the seed value.
guides\dataset\run_retrieval_test.md
---
sidebar_position: 10
slug: /run_retrieval_test
---
# Run retrieval test
Conduct a retrieval test on your knowledge base to check whether the intended chunks can be retrieved.
---
After your files are uploaded and parsed, it is recommended that you run a retrieval test before proceeding with the chat assistant configuration. Running a retrieval test is *not* an unnecessary or superfluous step at all! Just like fine-tuning a precision instrument, RAGFlow requires careful tuning to deliver optimal question answering performance. Your knowledge base settings, chat assistant configurations, and the specified large and small models can all significantly impact the final results. Running a retrieval test verifies whether the intended chunks can be recovered, allowing you to quickly identify areas for improvement or pinpoint any issue that needs addressing. For instance, when debugging your question answering system, if you know that the correct chunks can be retrieved, you can focus your efforts elsewhere. For example, in issue [#5627](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/issues/5627), the problem was found to be due to the LLM's limitations.
During a retrieval test, chunks created from your specified chunking method are retrieved using a hybrid search. This search combines weighted keyword similarity with either weighted vector cosine similarity or a weighted reranking score, depending on your settings:
- If no rerank model is selected, weighted keyword similarity will be combined with weighted vector cosine similarity.
- If a rerank model is selected, weighted keyword similarity will be combined with weighted vector reranking score.
In contrast, chunks created from [knowledge graph construction](./construct_knowledge_graph.md) are retrieved solely using vector cosine similarity.
## Prerequisites
- Your files are uploaded and successfully parsed before running a retrieval test.
- A knowledge graph must be successfully built before enabling **Use knowledge graph**.
## Configurations
### Similarity threshold
This sets the bar for retrieving chunks: chunks with similarities below the threshold will be filtered out. By default, the threshold is set to 0.2. This means that only chunks with hybrid similarity score of 20 or higher will be retrieved.
### Keyword similarity weight
This sets the weight of keyword similarity in the combined similarity score, whether used with vector cosine similarity or a reranking score. By default, it is set to 0.7, making the weight of the other component 0.3 (1 - 0.7).
### Rerank model
- If left empty, RAGFlow will use a combination of weighted keyword similarity and weighted vector cosine similarity.
- If a rerank model is selected, weighted keyword similarity will be combined with weighted vector reranking score.
:::danger IMPORTANT
Using a rerank model will significantly increase the time to receive a response.
:::
### Use knowledge graph
In a knowledge graph, an entity description, a relationship description, or a community report each exists as an independent chunk. This switch indicates whether to add these chunks to the retrieval.
The switch is disabled by default. When enabled, RAGFlow performs the following during a retrieval test:
1. Extract entities and entity types from your query using the LLM.
2. Retrieve top N entities from the graph based on their PageRank values, using the extracted entity types.
3. Find similar entities and their N-hop relationships from the graph using the embeddings of the extracted query entities.
4. Retrieve similar relationships from the graph using the query embedding.
5. Rank these retrieved entities and relationships by multiplying each one's PageRank value with its similarity score to the query, returning the top n as the final retrieval.
6. Retrieve the report for the community involving the most entities in the final retrieval.
*The retrieved entity descriptions, relationship descriptions, and the top 1 community report are sent to the LLM for content generation.*
:::danger IMPORTANT
Using a knowledge graph in a retrieval test will significantly increase the time to receive a response.
:::
### Test text
This field is where you put in your testing query.
## Procedure
1. Navigate to the **Retrieval testing** page of your knowledge base, enter your query in **Test text**, and click **Testing** to run the test.
2. If the results are unsatisfactory, tune the options listed in the Configuration section and rerun the test.
*The following is a screenshot of a retrieval test conducted without using knowledge graph. It demonstrates a hybrid search combining weighted keyword similarity and weighted vector cosine similarity. The overall hybrid similarity score is 28.56, calculated as 25.17 (term similarity score) x 0.7 + 36.49 (vector similarity score) x 0.3:*

*The following is a screenshot of a retrieval test conducted using a knowledge graph. It shows that only vector similarity is used for knowledge graph-generated chunks:*

:::caution WARNING
If you have adjusted the default settings, such as keyword similarity weight or similarity threshold, to achieve the optimal results, be aware that these changes will not be automatically saved. You must apply them to your chat assistant settings or the **Retrieval** agent component settings.
:::
## Frequently asked questions
### Is an LLM used when the Use Knowledge Graph switch is enabled?
Yes, your LLM will be involved to analyze your query and extract the related entities and relationship from the knowledge graph. This also explains why additional tokens and time will be consumed.
guides\dataset\set_metadata.md
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /set_metada
---
# Set metadata
Add metadata to an uploaded file
---
On the **Dataset** page of your knowledge base, you can add metadata to any uploaded file. This approach enables you to 'tag' additional information like URL, author, date, and more to an existing file or dataset. In an AI-powered chat, such information will be sent to the LLM with the retrieved chunks for content generation.
For example, if you have a dataset of HTML files and want the LLM to cite the source URL when responding to your query, add a `"url"` parameter to each file's metadata.

:::tip NOTE
Ensure that your metadata is in JSON format; otherwise, your updates will not be applied.
:::

guides\dataset\set_page_rank.md
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /set_page_rank
---
# Set page rank
Create a step-retrieval strategy using page rank.
---
## Scenario
In an AI-powered chat, you can configure a chat assistant or an agent to respond using knowledge retrieved from multiple specified knowledge bases (datasets), provided that they employ the same embedding model. In situations where you prefer information from certain knowledge base(s) to take precedence or to be retrieved first, you can use RAGFlow's page rank feature to increase the ranking of chunks from these knowledge bases. For example, if you have configured a chat assistant to draw from two knowledge bases, knowledge base A for 2024 news and knowledge base B for 2023 news, but wish to prioritize news from year 2024, this feature is particularly useful.
:::info NOTE
It is important to note that this 'page rank' feature operates at the level of the entire knowledge base rather than on individual files or documents.
:::
## Configuration
On the **Configuration** page of your knowledge base, drag the slider under **Page rank** to set the page rank value for your knowledge base. You are also allowed to input the intended page rank value in the field next to the slider.
:::info NOTE
The page rank value must be an integer. Range: [0,100]
- 0: Disabled (Default)
- A specific value: enabled
:::
:::tip NOTE
If you set the page rank value to a non-integer, say 1.7, it will be rounded down to the nearest integer, which in this case is 1.
:::
## Scoring mechanism
If you configure a chat assistant's **similarity threshold** to 0.2, only chunks with a hybrid score greater than 0.2 x 100 = 20 will be retrieved and sent to the chat model for content generation. This initial filtering step is crucial for narrowing down relevant information.
If you have assigned a page rank of 1 to knowledge base A (2024 news) and 0 to knowledge base B (2023 news), the final hybrid scores of the retrieved chunks will be adjusted accordingly. A chunk retrieved from knowledge base A with an initial score of 50 will receive a boost of 1 x 100 = 100 points, resulting in a final score of 50 + 1 x 100 = 150. In this way, chunks retrieved from knowledge base A will always precede chunks from knowledge base B.
guides\dataset\use_tag_sets.md
---
sidebar_position: 6
slug: /use_tag_sets
---
# Use tag set
Use a tag set to tag chunks in your datasets.
---
Retrieval accuracy is the touchstone for a production-ready RAG framework. In addition to retrieval-enhancing approaches like auto-keyword, auto-question, and knowledge graph, RAGFlow introduces an auto-tagging feature to address semantic gaps. The auto-tagging feature automatically maps tags in the user-defined tag sets to relevant chunks within your knowledge base based on similarity with each chunk. This automation mechanism allows you to apply an additional "layer" of domain-specific knowledge to existing datasets, which is particularly useful when dealing with a large number of chunks.
To use this feature, ensure you have at least one properly configured tag set, specify the tag set(s) on the **Configuration** page of your knowledge base (dataset), and then re-parse your documents to initiate the auto-tagging process. During this process, each chunk in your dataset is compared with every entry in the specified tag set(s), and tags are automatically applied based on similarity.
:::caution NOTE
The auto-tagging feature is *unavailable* on the [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity) document engine.
:::
## Scenarios
Auto-tagging applies in situations where chunks are so similar to each other that the intended chunks cannot be distinguished from the rest. For example, when you have a few chunks about iPhone and a majority about iPhone case or iPhone accessaries, it becomes difficult to retrieve those chunks about iPhone without additional information.
## Create tag set
You can consider a tag set as a closed set, and the tags to attach to the chunks in your dataset (knowledge base) are *exclusively* from the specified tag set. You use a tag set to "inform" RAGFlow which chunks to tag and which tags to apply.
### Prepare a tag table file
A tag set can comprise one or multiple table files in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats. Each table file in the tag set contains two columns, **Description** and **Tag**:
- The first column provides descriptions of the tags listed in the second column. These descriptions can be example chunks or example queries. Similarity will be calculated between each entry in this column and every chunk in your dataset.
- The **Tag** column includes tags to pair with the description entries. Multiple tags should be separated by a comma (,).
:::tip NOTE
As a rule of thumb, consider including the following entries in your tag table:
- Descriptions of intended chunks, along with their corresponding tags.
- User queries that fail to retrieve the correct responses using other methods, ensuring their tags match the intended chunks in your dataset.
:::
### Create a tag set
1. Click **+ Create knowledge base** to create a knowledge base.
2. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of the created knowledge base and choose **Tag** as the default chunking method.
3. Navigate to the **Dataset** page and upload and parse your table file in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats.
_A tag cloud appears under the **Tag view** section, indicating the tag set is created:_

4. Click the **Table** tab to view the tag frequency table:

:::danger IMPORTANT
A tag set is *not* involved in document indexing or retrieval. Do not specify a tag set when configuring your chat assistant or agent.
:::
## Tag chunks
Once a tag set is created, you can apply it to your dataset:
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of your knowledge base (dataset).
2. Select the tag set from the **Tag sets** dropdown and click **Save** to confirm.
:::tip NOTE
If the tag set is missing from the dropdown, check that it has been created or configured correctly.
:::
3. Re-parse your documents to start the auto-tagging process.
_In an AI chat scenario using auto-tagged datasets, each query will be tagged using the corresponding tag set(s) and chunks with these tags will have a higher chance to be retrieved._
## Update tag set
Creating a tag set is *not* for once and for all. Oftentimes, you may find it necessary to update or delete existing tags or add new entries.
- You can update the existing tag set in the tag frequency table.
- To add new entries, you can add and parse new table files in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats.
### Update tag set in tag frequency table
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page in your tag set.
2. Click the **Table** tab under **Tag view** to view the tag frequncy table, where you can update tag names or delete tags.
:::danger IMPORTANT
When a tag set is updated, you must re-parse the documents in your dataset so that their tags can be updated accordingly.
:::
### Add new table files
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page in your tag set.
2. Navigate to the **Dataset** page and upload and parse your table file in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats.
:::danger IMPORTANT
If you add new table files to your tag set, it is at your own discretion whether to re-parse your documents in your datasets.
:::
## Frequently asked questions
### Can I reference more than one tag set?
Yes, you can. Usually one tag set suffices. When using multiple tag sets, ensure they are independent of each other; otherwise, consider merging your tag sets.
### Difference between a tag set and a standard knowledge base?
A standard knowledge base is a dataset. It will be searched by RAGFlow's document engine and the retrieved chunks will be fed to the LLM. In contrast, a tag set is used solely to attach tags to chunks within your dataset. It does not directly participate in the retrieval process, and you should not choose a tag set when selecting datasets for your chat assistant or agent.
### Difference between auto-tag and auto-keyword?
Both features enhance retrieval in RAGFlow. The auto-keyword feature relies on the LLM and consumes a significant number of tokens, whereas the auto-tag feature is based on vector similarity and predefined tag set(s). You can view the keywords applied in the auto-keyword feature as an open set, as they are generated by the LLM. In contrast, a tag set can be considered a user-defined close set, requiring upload tag set(s) in specified formats before use.
guides\dataset\best_practices_category_.json
{
"label": "Best practices",
"position": 11,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Best practices on configuring a knowledge base."
}
}
guides\dataset\best_practices\accelerate_doc_indexing.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /accelerate_doc_indexing
---
# Accelerate indexing
import APITable from '@site/src/components/APITable';
A checklist to speed up document parsing and indexing.
---
Please note that some of your settings may consume a significant amount of time. If you often find that document parsing is time-consuming, here is a checklist to consider:
- Use GPU to reduce embedding time.
- On the configuration page of your knowledge base, switch off **Use RAPTOR to enhance retrieval**.
- Extracting knowledge graph (GraphRAG) is time-consuming.
- Disable **Auto-keyword** and **Auto-question** on the configuration page of your knowledge base, as both depend on the LLM.
- **v0.17.0+:** If your document is plain text PDF and does not require GPU-intensive processes like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), TSR (Table Structure Recognition), or DLA (Document Layout Analysis), you can choose **Naive** over **DeepDoc** or other time-consuming large model options in the **Document parser** dropdown. This will substantially reduce document parsing time.
guides\models_category_.json
{
"label": "Models",
"position": -1,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Guides on model settings."
}
}
guides\models\llm_api_key_setup.md
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /llm_api_key_setup
---
# Configure model API key
An API key is required for RAGFlow to interact with an online AI model. This guide provides information about setting your model API key in RAGFlow.
## Get model API key
RAGFlow supports most mainstream LLMs. Please refer to [Supported Models](../../references/supported_models.mdx) for a complete list of supported models. You will need to apply for your model API key online. Note that most LLM providers grant newly-created accounts trial credit, which will expire in a couple of months, or a promotional amount of free quota.
:::note
If you find your online LLM is not on the list, don't feel disheartened. The list is expanding, and you can [file a feature request](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/issues/new?assignees=&labels=feature+request&projects=&template=feature_request.yml&title=%5BFeature+Request%5D%3A+) with us! Alternatively, if you have customized or locally-deployed models, you can [bind them to RAGFlow using Ollama, Xinference, or LocalAI](./deploy_local_llm.mdx).
:::
## Configure model API key
You have two options for configuring your model API key:
- Configure it in **service_conf.yaml.template** before starting RAGFlow.
- Configure it on the **Model providers** page after logging into RAGFlow.
### Configure model API key before starting up RAGFlow
1. Navigate to **./docker/ragflow**.
2. Find entry **user_default_llm**:
- Update `factory` with your chosen LLM.
- Update `api_key` with yours.
- Update `base_url` if you use a proxy to connect to the remote service.
3. Reboot your system for your changes to take effect.
4. Log into RAGFlow.
_After logging into RAGFlow, you will find your chosen model appears under **Added models** on the **Model providers** page._
### Configure model API key after logging into RAGFlow
:::caution WARNING
After logging into RAGFlow, configuring your model API key through the **service_conf.yaml.template** file will no longer take effect.
:::
After logging into RAGFlow, you can *only* configure API Key on the **Model providers** page:
1. Click on your logo on the top right of the page **>** **Model providers**.
2. Find your model card under **Models to be added** and click **Add the model**:

3. Paste your model API key.
4. Fill in your base URL if you use a proxy to connect to the remote service.
5. Click **OK** to confirm your changes.
:::note
To update an existing model API key at a later point:

:::
guides\team_category_.json
{
"label": "Team",
"position": 4,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Team-specific guides."
}
}
guides\team\join_or_leave_team.md
---
sidebar_position: 2
slug: /join_or_leave_team
---
# Join or leave a team
Accept an invite to join a team, decline an invite, or leave a team.
---
Once you join a team, you can do the following:
- Upload documents to the team owner's shared datasets (knowledge bases).
- Parse documents in the team owner's shared datasets.
- Use the team owner's shared Agents.
:::tip NOTE
You cannot invite users to a team unless you are its owner.
:::
## Prerequisites
1. Ensure that your Email address that received the team invitation is associated with a RAGFlow user account.
2. The team owner should share his knowledge bases by setting their **Permission** to **Team**.
## Accept or decline team invite
1. You will be notified when you receive an invitation to join a team:
2. Click on your avatar in the top right corner of the page, then select **Team** in the left-hand panel to access the **Team** page.

_On the **Team** page, you can view the information about members of your team and the teams you have joined._

_After accepting the team invite, you should be able to view and update the team owner's knowledge bases whose **Permissions** is set to **Team**._
## Leave a joined team
guides\team\manage_team_members.md
---
sidebar_position: 1
slug: /manage_team_members
---
# Manage team members
Invite or remove team members.
---
By default, each RAGFlow user is assigned a single team named after their name. RAGFlow allows you to invite RAGFlow users to your team. Your team members can help you:
- Upload documents to your shared datasets (knowledge bases).
- Parse documents in your shared datasets.
- Use your shared Agents.
:::tip NOTE
- Your team members are currently *not* allowed to invite users to your team, and only you, the team owner, is permitted to do so.
- Sharing added models with team members is only available in RAGFlow's Enterprise edition.
:::
## Prerequisites
1. Ensure that the invited team member is a RAGFlow user and that the Email address used is associated with a RAGFlow user account.
2. To allow your team members to view and update your knowledge base, ensure that you set **Permissions** on its **Configuration** page from **Only me** to **Team**.
## Invite team members
Click on your avatar in the top right corner of the page, then select **Team** in the left-hand panel to access the **Team** page.

_On the **Team** page, you can view the information about members of your team and the teams you have joined._
You are, by default, the owner of your own team and the only person permitted to invite users to join your team or remove team members.

## Remove team members

guides\team\share_agents.md
---
sidebar_position: 5
slug: /share_agent
---
# Share Agent
Share an Agent with your team members.
---
When ready, you may share your Agents with your team members so that they can use them. Please note that your Agents are not shared automatically; you must manually enable sharing by selecting the corresponding **Permissions** radio button:
1. Click the intended Agent to open its editing canvas.
2. Click **Settings** to show the **Agent settings** dialogue.
3. Change **Permissions** from **Only me** to **Team**.
4. Click **Save** to apply your changes.
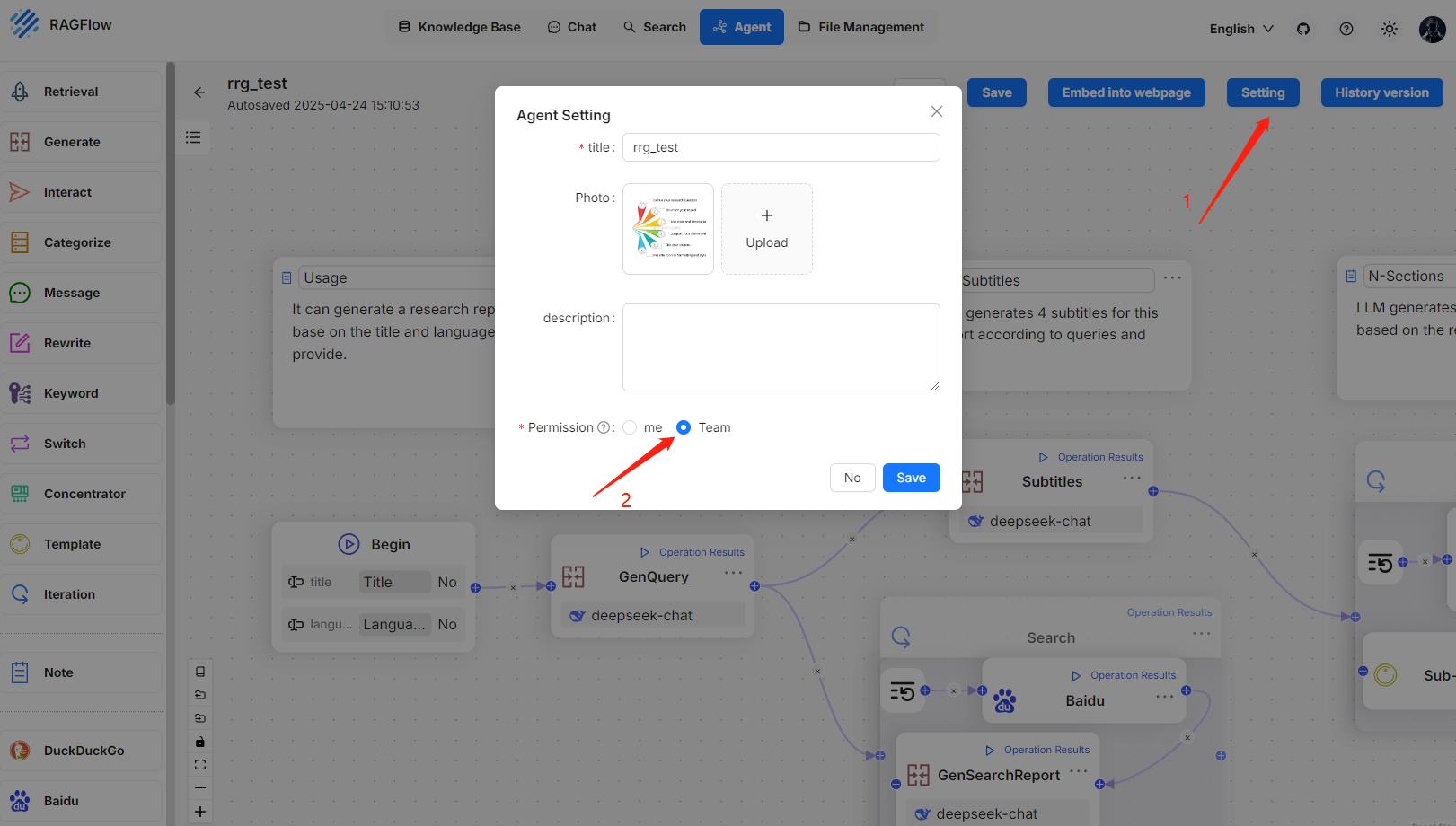
*When completed, your team members will see your shared Agents like this:*
guides\team\share_chat_assistant.md
---
sidebar_position: 4
slug: /share_chat_assistant
---
# Share chat assistant
Sharing chat assistant is currently exclusive to RAGFlow Enterprise, but will be made available in due course.
guides\team\share_knowledge_bases.md
---
sidebar_position: 3
slug: /share_datasets
---
# Share knowledge base
Share a knowledge base with team members.
---
When ready, you may share your knowledge bases with your team members so that they can upload and parse files in them. Please note that your knowledge bases are not shared automatically; you must manually enable sharing by selecting the appropriate **Permissions** radio button:
1. Navigate to the knowledge base's **Configuration** page.
2. Change **Permissions** from **Only me** to **Team**.
3. Click **Save** to apply your changes.
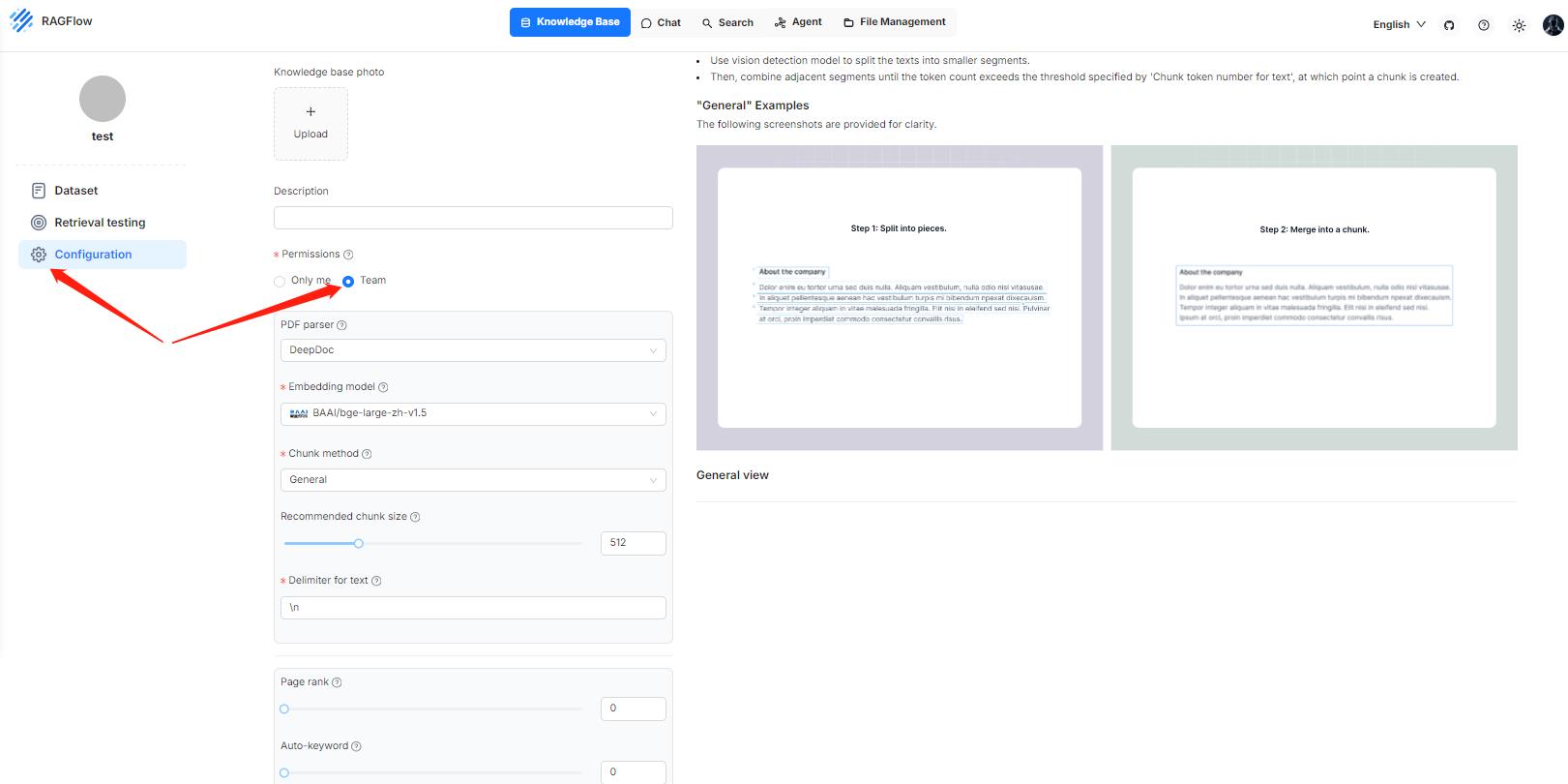
*Once completed, your team members will see your shared knowledge bases like this:*
guides\team\share_model.md
---
sidebar_position: 6
slug: /share_model
---
# Share models
Sharing models is currently exclusive to RAGFlow Enterprise.
references_category_.json
{
"label": "References",
"position": 6,
"link": {
"type": "generated-index",
"description": "Miscellaneous References"
}
}
references\supported_models.mdx
---
sidebar_position: 0
slug: /supported_models
---
# Supported models
import APITable from '@site/src/components/APITable';
A complete list of models supported by RAGFlow, which will continue to expand.
```mdx-code-block
<APITable>
```
| Provider | Chat | Embedding | Rerank | Img2txt | Speech2txt | TTS |
| --------------------- | ------------------ | ------------------ | ------------------ | ------------------ | ------------------ | ------------------ |
| Anthropic | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| Azure-OpenAI | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | |
| BAAI | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | |
| BaiChuan | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| BaiduYiyan | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| Bedrock | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| Cohere | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| DeepSeek | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| FastEmbed | | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| Fish Audio | | | | | | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Gemini | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| Google Cloud | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| GPUStack | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Groq | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| HuggingFace | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| Jina | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | |
| LeptonAI | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| LocalAI | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| LM-Studio | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| MiniMax | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| Mistral | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| ModelScope | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| Moonshot | :heavy_check_mark: | | | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| Novita AI | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| NVIDIA | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| Ollama | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| OpenAI | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| OpenAI-API-Compatible | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| OpenRouter | :heavy_check_mark: | | | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| PerfXCloud | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| Replicate | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| PPIO | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| SILICONFLOW | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| StepFun | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| Tencent Hunyuan | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| Tencent Cloud | | | | | :heavy_check_mark: | |
| TogetherAI | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| Tongyi-Qianwen | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Upstage | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | |
| VLLM | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| VolcEngine | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
| Voyage AI | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| Xinference | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
| XunFei Spark | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | :heavy_check_mark: |
| Youdao | | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | | |
| ZHIPU-AI | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | | :heavy_check_mark: | | |
| 01.AI | :heavy_check_mark: | | | | | |
```mdx-code-block
</APITable>
```
:::danger IMPORTANT
If your model is not listed here but has APIs compatible with those of OpenAI, click **OpenAI-API-Compatible** on the **Model providers** page to configure your model.
:::
:::note
The list of supported models is extracted from [this source](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/blob/main/rag/llm/__init__.py) and may not be the most current. For the latest supported model list, please refer to the Python file.
:::